Mathematics
Mathematicians seek and use patterns[8][9] to formulate new conjectures; they resolve the truth or falsity of such by mathematical proof. When mathematical structures are good models of real phenomena, mathematical reasoning can be used to provide insight or predictions about nature. Through the use of abstraction and logic, mathematics developed from counting, calculation, measurement, and the systematic study of the shapes and motions of physical objects. Practical mathematics has been a human activity from as far back as written records exist. The research required to solve mathematical problems can take years or even centuries of sustained inquiry.Mathematics (from Greek: μάθημα, máthēma, 'knowledge, study, learning') includes the study of such topics as quantity (number theory),[1] structure (algebra),[2] space (geometry),[1] and change (mathematical analysis).[3][4][5] It has no generally accepted definition.[6][7]
Rigorous arguments first appeared in Greek mathematics, most notably in Euclid's Elements.[10] Since the pioneering work of Giuseppe Peano (1858–1932), David Hilbert (1862–1943), and others on axiomatic systems in the late 19th century, it has become customary to view mathematical research as establishing truth by rigorous deduction from appropriately chosen axioms and definitions. Mathematics developed at a relatively slow pace until the Renaissance, when mathematical innovations interacting with new scientific discoveries led to a rapid increase in the rate of mathematical discovery that has continued to the present day.[11]
Mathematics is essential in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, finance, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics has led to entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians engage in pure mathematics (mathematics for its own sake) without having any application in mind, but practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered later.[12][13]
History
The history of mathematics can be seen as an ever-increasing series of abstractions. The first abstraction, which is shared by many animals,[14] was probably that of numbers: the realization that a collection of two apples and a collection of two oranges (for example) have something in common, namely quantity of their members.
As evidenced by tallies found on bone, in addition to recognizing how to count physical objects, prehistoric peoples may have also recognized how to count abstract quantities, like time—days, seasons, or years.[15][16]
Evidence for more complex mathematics does not appear until around 3000 BC, when the Babylonians and Egyptians began using arithmetic, algebra and geometry for taxation and other financial calculations, for building and construction, and for astronomy.[17] The most ancient mathematical texts from Mesopotamia and Egypt are from 2000–1800 BC.[18] Many early texts mention Pythagorean triples and so, by inference, the Pythagorean theorem seems to be the most ancient and widespread mathematical development after basic arithmetic and geometry.[19] It is in Babylonian mathematics that elementary arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) first appear in the archaeological record. The Babylonians also possessed a place-value system, and used a sexagesimal numeral system [19] which is still in use today for measuring angles and time.[20]
Beginning in the 6th century BC with the Pythagoreans, the Ancient Greeks began a systematic study of mathematics as a subject in its own right with Greek mathematics.[21] Around 300 BC, Euclid introduced the axiomatic method still used in mathematics today, consisting of definition, axiom, theorem, and proof. His textbook Elements is widely considered the most successful and influential textbook of all time.[22] The greatest mathematician of antiquity is often held to be Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC) of Syracuse.[23] He developed formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of solids of revolution and used the method of exhaustion to calculate the area under the arc of a parabola with the summation of an infinite series, in a manner not too dissimilar from modern calculus.[24] Other notable achievements of Greek mathematics are conic sections (Apollonius of Perga, 3rd century BC),[25] trigonometry (Hipparchus of Nicaea (2nd century BC),[26] and the beginnings of algebra (Diophantus, 3rd century AD).[27]
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system and the rules for the use of its operations, in use throughout the world today, evolved over the course of the first millennium AD in India and were transmitted to the Western world via Islamic mathematics.[28] Other notable developments of Indian mathematics include the modern definition and approximation of sine and cosine,[28] and an early form of infinite series.
During the Golden Age of Islam, especially during the 9th and 10th centuries, mathematics saw many important innovations building on Greek mathematics. The most notable achievement of Islamic mathematics was the development of algebra. Other notable achievements of the Islamic period are advances in spherical trigonometry and the addition of the decimal point to the Arabic numeral system.[29][30] Many notable mathematicians from this period were Persian, such as Al-Khwarismi, Omar Khayyam and Sharaf al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī.
During the early modern period, mathematics began to develop at an accelerating pace in Western Europe. The development of calculus by Newton and Leibniz in the 17th century revolutionized mathematics.[31] Leonhard Euler was the most notable mathematician of the 18th century, contributing numerous theorems and discoveries.[32] Perhaps the foremost mathematician of the 19th century was the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss,[33] who made numerous contributions to fields such as algebra, analysis, differential geometry, matrix theory, number theory, and statistics. In the early 20th century, Kurt Gödel transformed mathematics by publishing his incompleteness theorems, which show in part that any consistent axiomatic system—if powerful enough to describe arithmetic—will contain true propositions that cannot be proved.[34]
Mathematics has since been greatly extended, and there has been a fruitful interaction between mathematics and science, to the benefit of both. Mathematical discoveries continue to be made today. According to Mikhail B. Sevryuk, in the January 2006 issue of the Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, "The number of papers and books included in the Mathematical Reviews database since 1940 (the first year of operation of MR) is now more than 1.9 million, and more than 75 thousand items are added to the database each year. The overwhelming majority of works in this ocean contain new mathematical theorems and their proofs."[35]
Etymology
The word mathematics comes from Ancient Greek máthēma (μάθημα), meaning "that which is learnt,"[36] "what one gets to know," hence also "study" and "science". The word for "mathematics" came to have the narrower and more technical meaning "mathematical study" even in Classical times.[37] Its adjective is mathēmatikós (μαθηματικός), meaning "related to learning" or "studious," which likewise further came to mean "mathematical." In particular, mathēmatikḗ tékhnē (μαθηματικὴ τέχνη; Latin: ars mathematica) meant "the mathematical art."
Similarly, one of the two main schools of thought in Pythagoreanism was known as the mathēmatikoi (μαθηματικοί)—which at the time meant "learners" rather than "mathematicians" in the modern sense.[38]
In Latin, and in English until around 1700, the term mathematics more commonly meant "astrology" (or sometimes "astronomy") rather than "mathematics"; the meaning gradually changed to its present one from about 1500 to 1800. This has resulted in several mistranslations. For example, Saint Augustine's warning that Christians should beware of mathematici, meaning astrologers, is sometimes mistranslated as a condemnation of mathematicians.[39]
The apparent plural form in English, like the French plural form les mathématiques (and the less commonly used singular derivative la mathématique), goes back to the Latin neuter plural mathematica (Cicero), based on the Greek plural ta mathēmatiká (τὰ μαθηματικά), used by Aristotle (384–322 BC), and meaning roughly "all things mathematical", although it is plausible that English borrowed only the adjective mathematic(al) and formed the noun mathematics anew, after the pattern of physics and metaphysics, which were inherited from Greek.[40] In English, the noun mathematics takes a singular verb. It is often shortened to maths or, in North America, math.[41]
Definitions of mathematics
Mathematics has no generally accepted definition.[6][7] Aristotle defined mathematics as "the science of quantity" and this definition prevailed until the 18th century. However, Aristotle also noted a focus on quantity alone may not distinguish mathematics from sciences like physics; in his view, abstraction and studying quantity as a property "separable in thought" from real instances set mathematics apart.[42]
In the 19th century, when the study of mathematics increased in rigor and began to address abstract topics such as group theory and projective geometry, which have no clear-cut relation to quantity and measurement, mathematicians and philosophers began to propose a variety of new definitions.[43]
A great many professional mathematicians take no interest in a definition of mathematics, or consider it undefinable.[6] There is not even consensus on whether mathematics is an art or a science.[7] Some just say, "Mathematics is what mathematicians do."[6]
Three leading types
Three leading types of definition of mathematics today are called logicist, intuitionist, and formalist, each reflecting a different philosophical school of thought.[44] All have severe flaws, none has widespread acceptance, and no reconciliation seems possible.[44]
Logicist definitions
An early definition of mathematics in terms of logic was that of Benjamin Peirce (1870): "the science that draws necessary conclusions."[45] In the Principia Mathematica, Bertrand Russell and Alfred North Whitehead advanced the philosophical program known as logicism, and attempted to prove that all mathematical concepts, statements, and principles can be defined and proved entirely in terms of symbolic logic. A logicist definition of mathematics is Russell's (1903) "All Mathematics is Symbolic Logic."[46]
Intuitionist definitions
Intuitionist definitions, developing from the philosophy of mathematician L. E. J. Brouwer, identify mathematics with certain mental phenomena. An example of an intuitionist definition is "Mathematics is the mental activity which consists in carrying out constructs one after the other."[44] A peculiarity of intuitionism is that it rejects some mathematical ideas considered valid according to other definitions. In particular, while other philosophies of mathematics allow objects that can be proved to exist even though they cannot be constructed, intuitionism allows only mathematical objects that one can actually construct. Intuitionists also reject the law of excluded middle (i.e., ). While this stance does force them to reject one common version of proof by contradiction as a viable proof method, namely the inference of from , they are still able to infer from . For them, is a strictly weaker statement than . [47]
Formalist definitions
Formalist definitions identify mathematics with its symbols and the rules for operating on them. Haskell Curry defined mathematics simply as "the science of formal systems".[48] A formal system is a set of symbols, or tokens, and some rules on how the tokens are to be combined into formulas. In formal systems, the word axiom has a special meaning different from the ordinary meaning of "a self-evident truth", and is used to refer to a combination of tokens that is included in a given formal system without needing to be derived using the rules of the system.
Mathematics as science
The German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss referred to mathematics as "the Queen of the Sciences".[49] More recently, Marcus du Sautoy has called mathematics "the Queen of Science ... the main driving force behind scientific discovery".[50] The philosopher Karl Popper observed that "most mathematical theories are, like those of physics and biology, hypothetico-deductive: pure mathematics therefore turns out to be much closer to the natural sciences whose hypotheses are conjectures, than it seemed even recently."[51] Popper also noted that "I shall certainly admit a system as empirical or scientific only if it is capable of being tested by experience."[52]
Several authors consider that mathematics is not a science because it does not rely on empirical evidence.[53][54][55][56]
Mathematics shares much in common with many fields in the physical sciences, notably the exploration of the logical consequences of assumptions. Intuition and experimentation also play a role in the formulation of conjectures in both mathematics and the (other) sciences. Experimental mathematics continues to grow in importance within mathematics, and computation and simulation are playing an increasing role in both the sciences and mathematics.
The opinions of mathematicians on this matter are varied. Many mathematicians[57] feel that to call their area a science is to downplay the importance of its aesthetic side, and its history in the traditional seven liberal arts; others feel that to ignore its connection to the sciences is to turn a blind eye to the fact that the interface between mathematics and its applications in science and engineering has driven much development in mathematics.[58] One way this difference of viewpoint plays out is in the philosophical debate as to whether mathematics is created (as in art) or discovered (as in science). In practice, mathematicians are typically grouped with scientists at the gross level but separated at finer levels. This is one of many issues considered in the philosophy of mathematics.[59]
Inspiration, pure and applied mathematics, and aesthetics
Mathematics arises from many different kinds of problems. At first these were found in commerce, land measurement, architecture and later astronomy; today, all sciences suggest problems studied by mathematicians, and many problems arise within mathematics itself. For example, the physicist Richard Feynman invented the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics using a combination of mathematical reasoning and physical insight, and today's string theory, a still-developing scientific theory which attempts to unify the four fundamental forces of nature, continues to inspire new mathematics.[60]
Some mathematics is relevant only in the area that inspired it, and is applied to solve further problems in that area. But often mathematics inspired by one area proves useful in many areas, and joins the general stock of mathematical concepts. A distinction is often made between pure mathematics and applied mathematics. However pure mathematics topics often turn out to have applications, e.g. number theory in cryptography. This remarkable fact, that even the "purest" mathematics often turns out to have practical applications, is what Eugene Wigner has called "the unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics".[13] As in most areas of study, the explosion of knowledge in the scientific age has led to specialization: there are now hundreds of specialized areas in mathematics and the latest Mathematics Subject Classification runs to 46 pages.[61] Several areas of applied mathematics have merged with related traditions outside of mathematics and become disciplines in their own right, including statistics, operations research, and computer science.
For those who are mathematically inclined, there is often a definite aesthetic aspect to much of mathematics. Many mathematicians talk about the elegance of mathematics, its intrinsic aesthetics and inner beauty. Simplicity and generality are valued. There is beauty in a simple and elegant proof, such as Euclid's proof that there are infinitely many prime numbers, and in an elegant numerical method that speeds calculation, such as the fast Fourier transform. G. H. Hardy in A Mathematician's Apology expressed the belief that these aesthetic considerations are, in themselves, sufficient to justify the study of pure mathematics. He identified criteria such as significance, unexpectedness, inevitability, and economy as factors that contribute to a mathematical aesthetic.[62] Mathematical research often seeks critical features of a mathematical object. A theorem expressed as a characterization of the object by these features is the prize. Examples of particularly succinct and revelatory mathematical arguments has been published in Proofs from THE BOOK.
The popularity of recreational mathematics is another sign of the pleasure many find in solving mathematical questions. And at the other social extreme, philosophers continue to find problems in philosophy of mathematics, such as the nature of mathematical proof.[63]
Notation, language, and rigor
Most of the mathematical notation in use today was not invented until the 16th century.[64] Before that, mathematics was written out in words, limiting mathematical discovery.[65] Euler (1707–1783) was responsible for many of the notations in use today. Modern notation makes mathematics much easier for the professional, but beginners often find it daunting. According to Barbara Oakley, this can be attributed to the fact that mathematical ideas are both more abstract and more encrypted than those of natural language.[66] Unlike natural language, where people can often equate a word (such as cow) with the physical object it corresponds to, mathematical symbols are abstract, lacking any physical analog.[67] Mathematical symbols are also more highly encrypted than regular words, meaning a single symbol can encode a number of different operations or ideas.[68]
Mathematical language can be difficult to understand for beginners because even common terms, such as or and only, have a more precise meaning than they have in everyday speech, and other terms such as open and field refer to specific mathematical ideas, not covered by their laymen's meanings. Mathematical language also includes many technical terms such as homeomorphism and integrable that have no meaning outside of mathematics. Additionally, shorthand phrases such as iff for "if and only if" belong to mathematical jargon. There is a reason for special notation and technical vocabulary: mathematics requires more precision than everyday speech. Mathematicians refer to this precision of language and logic as "rigor".
Mathematical proof is fundamentally a matter of rigor. Mathematicians want their theorems to follow from axioms by means of systematic reasoning. This is to avoid mistaken "theorems", based on fallible intuitions, of which many instances have occurred in the history of the subject.[b] The level of rigor expected in mathematics has varied over time: the Greeks expected detailed arguments, but at the time of Isaac Newton the methods employed were less rigorous. Problems inherent in the definitions used by Newton would lead to a resurgence of careful analysis and formal proof in the 19th century. Misunderstanding the rigor is a cause for some of the common misconceptions of mathematics. Today, mathematicians continue to argue among themselves about computer-assisted proofs. Since large computations are hard to verify, such proofs may be erroneous if the used computer program is erroneous.[c][69] On the other hand, proof assistants allow verifying all details that cannot be given in a hand-written proof, and provide certainty of the correctness of long proofs such as that of the Feit–Thompson theorem.[d]
Axioms in traditional thought were "self-evident truths", but that conception is problematic.[70] At a formal level, an axiom is just a string of symbols, which has an intrinsic meaning only in the context of all derivable formulas of an axiomatic system. It was the goal of Hilbert's program to put all of mathematics on a firm axiomatic basis, but according to Gödel's incompleteness theorem every (sufficiently powerful) axiomatic system has undecidable formulas; and so a final axiomatization of mathematics is impossible. Nonetheless mathematics is often imagined to be (as far as its formal content) nothing but set theory in some axiomatization, in the sense that every mathematical statement or proof could be cast into formulas within set theory.[71]
Fields of mathematics
Mathematics can, broadly speaking, be subdivided into the study of quantity, structure, space, and change (i.e. arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and analysis). In addition to these main concerns, there are also subdivisions dedicated to exploring links from the heart of mathematics to other fields: to logic, to set theory (foundations), to the empirical mathematics of the various sciences (applied mathematics), and more recently to the rigorous study of uncertainty. While some areas might seem unrelated, the Langlands program has found connections between areas previously thought unconnected, such as Galois groups, Riemann surfaces and number theory.
Discrete mathematics conventionally groups together the fields of mathematics which study mathematical structures that are fundamentally discrete rather than continuous.
Foundations and philosophy
In order to clarify the foundations of mathematics, the fields of mathematical logic and set theory were developed. Mathematical logic includes the mathematical study of logic and the applications of formal logic to other areas of mathematics; set theory is the branch of mathematics that studies sets or collections of objects. The phrase "crisis of foundations" describes the search for a rigorous foundation for mathematics that took place from approximately 1900 to 1930.[72] Some disagreement about the foundations of mathematics continues to the present day. The crisis of foundations was stimulated by a number of controversies at the time, including the controversy over Cantor's set theory and the Brouwer–Hilbert controversy.
Mathematical logic is concerned with setting mathematics within a rigorous axiomatic framework, and studying the implications of such a framework. As such, it is home to Gödel's incompleteness theorems which (informally) imply that any effective formal system that contains basic arithmetic, if sound (meaning that all theorems that can be proved are true), is necessarily incomplete (meaning that there are true theorems which cannot be proved in that system). Whatever finite collection of number-theoretical axioms is taken as a foundation, Gödel showed how to construct a formal statement that is a true number-theoretical fact, but which does not follow from those axioms. Therefore, no formal system is a complete axiomatization of full number theory. Modern logic is divided into recursion theory, model theory, and proof theory, and is closely linked to theoretical computer science,[citation needed] as well as to category theory. In the context of recursion theory, the impossibility of a full axiomatization of number theory can also be formally demonstrated as a consequence of the MRDP theorem.
Theoretical computer science includes computability theory, computational complexity theory, and information theory. Computability theory examines the limitations of various theoretical models of the computer, including the most well-known model—the Turing machine. Complexity theory is the study of tractability by computer; some problems, although theoretically solvable by computer, are so expensive in terms of time or space that solving them is likely to remain practically unfeasible, even with the rapid advancement of computer hardware. A famous problem is the "P = NP?" problem, one of the Millennium Prize Problems.[73] Finally, information theory is concerned with the amount of data that can be stored on a given medium, and hence deals with concepts such as compression and entropy.
Pure mathematics
Quantity
The study of quantity starts with numbers, first the familiar natural numbers and integers ("whole numbers") and arithmetical operations on them, which are characterized in arithmetic. The deeper properties of integers are studied in number theory, from which come such popular results as Fermat's Last Theorem. The twin prime conjecture and Goldbach's conjecture are two unsolved problems in number theory.
As the number system is further developed, the integers are recognized as a subset of the rational numbers ("fractions"). These, in turn, are contained within the real numbers, which are used to represent continuous quantities. Real numbers are generalized to complex numbers. These are the first steps of a hierarchy of numbers that goes on to include quaternions and octonions. Consideration of the natural numbers also leads to the transfinite numbers, which formalize the concept of "infinity". According to the fundamental theorem of algebra all solutions of equations in one unknown with complex coefficients are complex numbers, regardless of degree. Another area of study is the size of sets, which is described with the cardinal numbers. These include the aleph numbers, which allow meaningful comparison of the size of infinitely large sets.
Structure
Many mathematical objects, such as sets of numbers and functions, exhibit internal structure as a consequence of operations or relations that are defined on the set. Mathematics then studies properties of those sets that can be expressed in terms of that structure; for instance number theory studies properties of the set of integers that can be expressed in terms of arithmetic operations. Moreover, it frequently happens that different such structured sets (or structures) exhibit similar properties, which makes it possible, by a further step of abstraction, to state axioms for a class of structures, and then study at once the whole class of structures satisfying these axioms. Thus one can study groups, rings, fields and other abstract systems; together such studies (for structures defined by algebraic operations) constitute the domain of abstract algebra.
By its great generality, abstract algebra can often be applied to seemingly unrelated problems; for instance a number of ancient problems concerning compass and straightedge constructions were finally solved using Galois theory, which involves field theory and group theory. Another example of an algebraic theory is linear algebra, which is the general study of vector spaces, whose elements called vectors have both quantity and direction, and can be used to model (relations between) points in space. This is one example of the phenomenon that the originally unrelated areas of geometry and algebra have very strong interactions in modern mathematics. Combinatorics studies ways of enumerating the number of objects that fit a given structure.
Space
The study of space originates with geometry—in particular, Euclidean geometry, which combines space and numbers, and encompasses the well-known Pythagorean theorem. Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles and with the trigonometric functions. The modern study of space generalizes these ideas to include higher-dimensional geometry, non-Euclidean geometries (which play a central role in general relativity) and topology. Quantity and space both play a role in analytic geometry, differential geometry, and algebraic geometry. Convex and discrete geometry were developed to solve problems in number theory and functional analysis but now are pursued with an eye on applications in optimization and computer science. Within differential geometry are the concepts of fiber bundles and calculus on manifolds, in particular, vector and tensor calculus. Within algebraic geometry is the description of geometric objects as solution sets of polynomial equations, combining the concepts of quantity and space, and also the study of topological groups, which combine structure and space. Lie groups are used to study space, structure, and change. Topology in all its many ramifications may have been the greatest growth area in 20th-century mathematics; it includes point-set topology, set-theoretic topology, algebraic topology and differential topology. In particular, instances of modern-day topology are metrizability theory, axiomatic set theory, homotopy theory, and Morse theory. Topology also includes the now solved Poincaré conjecture, and the still unsolved areas of the Hodge conjecture. Other results in geometry and topology, including the four color theorem and Kepler conjecture, have been proven only with the help of computers.
Change
Understanding and describing change is a common theme in the natural sciences, and calculus was developed as a tool to investigate it. Functions arise here, as a central concept describing a changing quantity. The rigorous study of real numbers and functions of a real variable is known as real analysis, with complex analysis the equivalent field for the complex numbers. Functional analysis focuses attention on (typically infinite-dimensional) spaces of functions. One of many applications of functional analysis is quantum mechanics. Many problems lead naturally to relationships between a quantity and its rate of change, and these are studied as differential equations. Many phenomena in nature can be described by dynamical systems; chaos theory makes precise the ways in which many of these systems exhibit unpredictable yet still deterministic behavior.
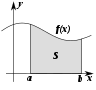 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Calculus | Vector calculus | Differential equations | Dynamical systems | Chaos theory | Complex analysis |
Applied mathematics
Applied mathematics concerns itself with mathematical methods that are typically used in science, engineering, business, and industry. Thus, "applied mathematics" is a mathematical science with specialized knowledge. The term applied mathematics also describes the professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems; as a profession focused on practical problems, applied mathematics focuses on the "formulation, study, and use of mathematical models" in science, engineering, and other areas of mathematical practice.
In the past, practical applications have motivated the development of mathematical theories, which then became the subject of study in pure mathematics, where mathematics is developed primarily for its own sake. Thus, the activity of applied mathematics is vitally connected with research in pure mathematics.
Statistics and other decision sciences
Applied mathematics has significant overlap with the discipline of statistics, whose theory is formulated mathematically, especially with probability theory. Statisticians (working as part of a research project) "create data that makes sense" with random sampling and with randomized experiments;[74] the design of a statistical sample or experiment specifies the analysis of the data (before the data becomes available). When reconsidering data from experiments and samples or when analyzing data from observational studies, statisticians "make sense of the data" using the art of modelling and the theory of inference—with model selection and estimation; the estimated models and consequential predictions should be tested on new data.[e]
Statistical theory studies decision problems such as minimizing the risk (expected loss) of a statistical action, such as using a procedure in, for example, parameter estimation, hypothesis testing, and selecting the best. In these traditional areas of mathematical statistics, a statistical-decision problem is formulated by minimizing an objective function, like expected loss or cost, under specific constraints: For example, designing a survey often involves minimizing the cost of estimating a population mean with a given level of confidence.[75] Because of its use of optimization, the mathematical theory of statistics shares concerns with other decision sciences, such as operations research, control theory, and mathematical economics.[76]
Computational mathematics
Computational mathematics proposes and studies methods for solving mathematical problems that are typically too large for human numerical capacity. Numerical analysis studies methods for problems in analysis using functional analysis and approximation theory; numerical analysis includes the study of approximation and discretisation broadly with special concern for rounding errors. Numerical analysis and, more broadly, scientific computing also study non-analytic topics of mathematical science, especially algorithmic matrix and graph theory. Other areas of computational mathematics include computer algebra and symbolic computation.











































No comments:
Post a Comment