Homo sapiens
| Homo sapiens | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Male and female H. s. sapiens (Akha in northern Thailand, 2007 photograph) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Subfamily: | Homininae |
| Tribe: | Hominini |
| Genus: | Homo |
| Species: | H. sapiens |
| Binomial name | |
| Homo sapiens | |
| Subspecies | |
H. s. sapiens | |
Homo sapiens (from Latin: homō, 'human being' + sapiēns, 'wise, sensible, judicious') is the only extant human species, all of whose members are of the subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens.[2][3][4] The name is Latin for wise man, and was introduced in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus (who is himself the lectotype for the species).
Extinct species of the genus Homo include Homo erectus (extant from roughly 2 to 0.1 million years ago) and a number of other species (by some authors considered subspecies of either H. sapiens or H. erectus). The divergence of the lineage leading to H. sapiens out of ancestral H. erectus (or an intermediate species such as Homo antecessor) is estimated to have occurred in Africa roughly 500,000 years ago. The earliest fossil evidence of early Homo sapiens appears in Africa around 300,000 years ago, with the earliest genetic splits among modern people, according to some evidence, dating to around the same time.[5][6][note 1][9] Sustained archaic admixture is known to have taken place both in Africa and (following the recent Out-Of-Africa expansion) in Eurasia, between about 100,000 and 30,000 years ago.[10]
The term anatomically modern humans (AMH)[11] is used to distinguish H. sapiens having an anatomy consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from varieties of extinct archaic humans. This is useful especially for times and regions where anatomically modern and archaic humans co-existed, for example, in Paleolithic Europe. As of 2017, the oldest known skeleton of an anatomically modern Homo sapiens is the Omo-Kibish I, which dates to about 196,000 years ago.[12]
Name and taxonomy
The binomial name Homo sapiens was coined by Linnaeus, 1758.[13] The Latin noun homō (genitive hominis) means "human being", while the participle sapiēns means "discerning, wise, sensible".
The species was initially thought to have emerged from a predecessor within the genus Homo around 300,000 to 200,000 years ago.[note 2] A problem with the morphological classification of "anatomically modern" was that it would not have included certain extant populations. For this reason, a lineage-based (cladistic) definition of H. sapiens has been suggested, in which H. sapiens would by definition refer to the modern human lineage following the split from the Neanderthal lineage. Such a cladistic definition would extend the age of H. sapiens to over 500,000 years.[note 3]
Estimates for the split between the Homo sapiens line and combined Neanderthal/Denisovan line range from between 503,000 and 565,000 years ago;[18] between 550,000 and 765,000 years ago;[19] and (based on rates of dental evolution) possibly more than 800,000 years ago.[20]
Extant human populations have historically been divided into subspecies, but since around the 1980s all extant groups have tended to be subsumed into a single species, H. sapiens, avoiding division into subspecies altogether.[note 4]
Some sources show Neanderthals (H. neanderthalensis) as a subspecies (H. sapiens neanderthalensis).[24][25] Similarly, the discovered specimens of the H. rhodesiensis species have been classified by some as a subspecies (H. sapiens rhodesiensis), although it remains more common to treat these last two as separate species within the genus Homo rather than as subspecies within H. sapiens.[26]
The subspecies H. sapiens sapiens is "modern humans" or "anatomically modern humans"—as humans exist today[2][3][4]—despite some, earlier uses of the term otherwise.[note 5] By the early 2000s, the subspecies H. s. sapiens became commonly recognized for the ancestral population of all contemporary humans, and as such it is equivalent to the binomial H. sapiens in the more restrictive sense (considering H. neanderthalensis a separate species).[note 6]
Age and speciation process
Derivation from H. erectus
The divergence of the lineage leading to H. sapiens out of archaic human varieties derived from H. erectus, is estimated as having taken place over 500,000 years ago.[9][6] Earlier studies estimated the oldest splits among modern populations to date around 160–100,000 years ago (in 2011 and 2012) on the basis of short-sequence fragments and to 300–250,000 years ago after rescaling (in 2012). However, the oldest split among modern human populations (such as the Khoisan split from other populations) was more recently calculated by a 2017 study to date between 350,000 and 260,000 years ago,[30][31] and the earliest known H. sapiens fossils also date to about that period, including the Jebel Irhoud remains from Morocco (ca. 300,000 or 350–280,000 years ago),[32] the Florisbad Skull from South Africa (ca. 259,000 years ago), and the Omo remains from Ethiopia (ca. 195,000 years ago).[33][34][35][36]
An mtDNA study in 2019 proposed an origin of modern humans in Botswana (and a Khoisan split) of around 200,000 years.[37] However, this proposal has been widely criticized by scholars,[38][39][40] with the recent evidence overall (genetic, fossil, and archaeological) supporting an origin for H. sapiens approximately 100,000 years earlier and in a broader region of Africa than the study proposes.[40]
In September 2019, scientists proposed that the earliest H. sapiens (and last common human ancestor to modern humans) arose between 350,000 and 260,000 years ago through a merging of populations in East and South Africa.[41][5]
An alternative suggestion defines H. sapiens cladistically as including the lineage of modern humans since the split from the lineage of Neanderthals, roughly 500,000 to 800,000 years ago.
The time of divergence between archaic H. sapiens and ancestors of Neanderthals and Denisovans caused by a genetic bottleneck of the latter was dated at 744,000 years ago, combined with repeated early admixture events and Denisovans diverging from Neanderthals 300 generations after their split from H. sapiens, as calculated by Rogers et al. (2017).[42]
The derivation of a comparatively homogeneous single species of H. sapiens from more diverse varieties of archaic humans (all of which were descended from the early dispersal of H. erectus some 1.8 million years ago) was debated in terms of two competing models during the 1980s: "recent African origin" postulated the emergence of H. sapiens from a single source population in Africa, which expanded and led to the extinction of all other human varieties, while the "multiregional evolution" model postulated the survival of regional forms of archaic humans, gradually converging into the modern human varieties by the mechanism of clinal variation, via genetic drift, gene flow and selection throughout the Pleistocene.[43]
Since the 2000s, the availability of data from archaeogenetics and population genetics has led to the emergence of a much more detailed picture, intermediate between the two competing scenarios outlined above: The recent Out-of-Africa expansion accounts for the predominant part of modern human ancestry, while there were also significant admixture events with regional archaic humans.[44][45]
Since the 1970s, the Omo remains, dated to some 195,000 years ago, have often been taken as the conventional cut-off point for the emergence of "anatomically modern humans". Since the 2000s, the discovery of older remains with comparable characteristics, and the discovery of ongoing hybridization between "modern" and "archaic" populations after the time of the Omo remains, have opened up a renewed debate on the age of H. sapiens in journalistic publications.[46][47][48][49][50] H. s. idaltu, dated to 160,000 years ago, has been postulated as an extinct subspecies of H. sapiens in 2003.[51][better source needed] H. neanderthalensis, which became extinct about 40,000 years ago, has also been classified as a subspecies, H. s. neanderthalensis.
H. heidelbergensis, dated 600,000 to 300,000 years ago, has long been thought to be a likely candidate for the last common ancestor of the Neanderthal and modern human lineages. However, genetic evidence from the Sima de los Huesos fossils published in 2016 seems to suggest that H. heidelbergensis in its entirety should be included in the Neanderthal lineage, as "pre-Neanderthal" or "early Neanderthal", while the divergence time between the Neanderthal and modern lineages has been pushed back to before the emergence of H. heidelbergensis, to close to 800,000 years ago, the approximate time of disappearance of H. antecessor.[52][53]
Early Homo sapiens
The term Middle Paleolithic is intended to cover the time between the first emergence of H. sapiens (roughly 300,000 years ago) and the emergence of full behavioral modernity (roughly by 50,000 years ago, corresponding to the start of the Upper Paleolithic).
Many of the early modern human finds, like those of Jebel Irhoud, Omo, Herto, Florisbad, Skhul, and Peștera cu Oase exhibit a mix of archaic and modern traits.[54][55][32] Skhul V, for example, has prominent brow ridges and a projecting face. However, the brain case is quite rounded and distinct from that of the Neanderthals and is similar to the brain case of modern humans. It is uncertain whether the robust traits of some of the early modern humans like Skhul V reflects mixed ancestry or retention of older traits.[56][57]
The "gracile" or lightly built skeleton of anatomically modern humans has been connected to a change in behavior, including increased cooperation and "resource transport".[58][59]
There is evidence that the characteristic human brain development, especially the prefrontal cortex, was due to "an exceptional acceleration of metabolome evolution ... paralleled by a drastic reduction in muscle strength. The observed rapid metabolic changes in brain and muscle, together with the unique human cognitive skills and low muscle performance, might reflect parallel mechanisms in human evolution."[60] The Schöningen spears and their correlation of finds are evidence that complex technological skills already existed 300,000 years ago, and are the first obvious proof of an active (big game) hunt. H. heidelbergensis already had intellectual and cognitive skills like anticipatory planning, thinking and acting that so far have only been attributed to modern man.[61][62]
The ongoing admixture events within anatomically modern human populations make it difficult to estimate the age of the matrilinear and patrilinear most recent common ancestors of modern populations (Mitochondrial Eve and Y-chromosomal Adam). Estimates of the age of Y-chromosomal Adam have been pushed back significantly with the discovery of an ancient Y-chromosomal lineage in 2013, to likely beyond 300,000 years ago.[note 7] There have, however, been no reports of the survival of Y-chromosomal or mitochondrial DNA clearly deriving from archaic humans (which would push back the age of the most recent patrilinear or matrilinear ancestor beyond 500,000 years).[64][65][66]
Fossil teeth found at Qesem Cave (Israel) and dated to between 400,000 and 200,000 years ago have been compared to the dental material from the younger (120,000–80,000 years ago) Skhul and Qafzeh hominins.[note 8]
Dispersal and archaic admixture
Dispersal of early H. sapiens begins soon after its emergence, as evidenced by the North African Jebel Irhoud finds (dated to around 315,000 years ago).[32][35] There is indirect evidence for H. sapiens presence in West Asia around 270,000 years ago.[68]
The Florisbad Skull from Florisbad, South Africa, dated to about 259,000 years ago, has also been classified as representing early H. sapiens.[33][34][36][5]
In September 2019, scientists proposed that the earliest H. sapiens (and last common human ancestor to modern humans) arose between 350,000 and 260,000 years ago through a merging of populations in East and South Africa.[41][5]
Among extant populations, the Khoi-San (or "Capoid") hunters-gatherers of Southern Africa may represent the human population with the earliest possible divergence within the group Homo sapiens sapiens. Their separation time has been estimated in a 2017 study to be between 350–260,000 years ago, compatible with the estimated age of early H. sapiens. The study states that the deep split-time estimation of 350 to 260 thousand years ago is consistent with the archaeological estimate for the onset of the Middle Stone Age across sub-Saharan Africa and coincides with archaic H. sapiens in southern Africa represented by, for example, the Florisbad skull dating to 259 (± 35) thousand years ago.[7]
H. s. idaltu, found at Middle Awash in Ethiopia, lived about 160,000 years ago,[69] and H. sapiens lived at Omo Kibish in Ethiopia about 195,000 years ago.[70] Two fossils from Goumde, Kenya, dated to at least (and likely more than) 180,000 years ago[33] and (more precisely) to 300–270,000 years ago,[5] have been tentatively assigned to H. sapiens and similarities have been noted between them and the Omo Kibbish remains.[33] Fossil evidence for modern human presence in West Asia is ascertained for 177,000 years ago,[71] and disputed fossil evidence suggests expansion as far as East Asia by 120,000 years ago.[72][73]
In July 2019, anthropologists reported the discovery of 210,000 year old remains of a H. sapiens and 170,000 year old remains of a H. neanderthalensis in Apidima Cave, Peloponnese, Greece, more than 150,000 years older than previous H. sapiens finds in Europe.[74][75][76]
A significant dispersal event, within Africa and to West Asia, is associated with the African megadroughts during MIS 5, beginning 130,000 years ago.[77] A 2011 study located the origin of basal population of contemporary human populations at 130,000 years ago, with the Khoi-San representing an "ancestral population cluster" located in southwestern Africa (near the coastal border of Namibia and Angola).[78]
While early modern human expansion in Sub-Saharan Africa before 130 kya persisted, early expansion to North Africa and Asia appears to have mostly disappeared by the end of MIS5 (75,000 years ago), and is known only from fossil evidence and from archaic admixture. Eurasia was re-populated by early modern humans in the so-called "recent out-of-Africa migration" post-dating MIS5, beginning around 70,000-50,000 years ago.[80][81][82][83] In this expansion, bearers of mt-DNA haplogroup L3 left East Africa, likely reaching Arabia via the Bab-el-Mandeb, and in the Great Coastal Migration spread to South Asia, Maritime South Asia and Oceania between 65,000-50,000 years ago,[84][85][86][87] while Europe, East and North Asia were reached by about 45,000 years ago. Some evidence suggests that an early wave humans may have reached the Americas by about 40–25,000 years ago.[citation needed]
Evidence for the overwhelming contribution of this "recent" (L3-derived) expansion to all non-African populations was established based on mitochondrial DNA, combined with evidence based on physical anthropology of archaic specimens, during the 1990s and 2000s,[note 9][89] and has also been supported by Y DNA and autosomal DNA.[83] The assumption of complete replacement has been revised in the 2010s with the discovery of admixture events (introgression) of populations of H. sapiens with populations of archaic humans over the period of between roughly 100,000 and 30,000 years ago, both in Eurasia and in Sub-Saharan Africa. Neanderthal admixture, in the range of 1-4%, is found in all modern populations outside of Africa, including in Europeans, Asians, Papua New Guineans, Australian Aboriginals, Native Americans, and other non-Africans.[90][44] This suggests that interbreeding between Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans took place after the recent "out of Africa" migration, likely between 60,000 and 40,000 years ago.[91][92][93] Recent admixture analyses have added to the complexity, finding that Eastern Neanderthals derive up to 2% of their ancestry from anatomically modern humans who left Africa some 100 kya.[94] The extent of Neanderthal admixture (and introgression of genes acquired by admixture) varies significantly between contemporary racial groups, being absent in Africans, intermediate in Europeans and highest in East Asians. Certain genes related to UV-light adaptation introgressed from Neanderthals have been found to have been selected for in East Asians specifically from 45,000 years ago until around 5,000 years ago.[95] The extent of archaic admixture is of the order of about 1% to 4% in Europeans and East Asians, and highest among Melanesians (the last also having Denisova hominin admixture at 4% to 6% in addition to neanderthal admixture).[44][56] Cumulatively, about 20% of the Neanderthal genome is estimated to remain present spread in contemporary populations.[96]
In September 2019, scientists reported the computerized determination, based on 260 CT scans, of a virtual skull shape of the last common human ancestor to modern humans/H. sapiens, representative of the earliest modern humans, and suggested that modern humans arose between 350,000 and 260,000 years ago through a merging of populations in East and South Africa while North-African fossils may represent a population which introgressed into Neandertals during the LMP.[41][5]
Anatomy
Generally, modern humans are more lightly built (or more "gracile") than the more "robust" archaic humans. Nevertheless, contemporary humans exhibit high variability in many physiological traits, and may exhibit remarkable "robustness". There are still a number of physiological details which can be taken as reliably differentiating the physiology of Neanderthals vs. anatomically modern humans.
Anatomical modernity
The term "anatomically modern humans" (AMH) is used with varying scope depending on context, to distinguish "anatomically modern" Homo sapiens from archaic humans such as Neanderthals and Middle and Lower Paleolithic hominins with transitional features intermediate between H. erectus, Neanderthals and early AMH called archaic Homo sapiens.[97] In a convention popular in the 1990s, Neanderthals were classified as a subspecies of H. sapiens, as H. s. neanderthalensis, while AMH (or European early modern humans, EEMH) was taken to refer to "Cro-Magnon" or H. s. sapiens. Under this nomenclature (Neanderthals considered H. sapiens), the term "anatomically modern Homo sapiens" (AMHS) has also been used to refer to EEMH ("Cro-Magnons").[98] It has since become more common to designate Neanderthals as a separate species, H. neanderthalensis, so that AMH in the European context refers to H. sapiens, but the question is by no means resolved.[note 10]
In this more narrow definition of H. sapiens, the subspecies Homo sapiens idaltu, discovered in 2003, also falls under the umbrella of "anatomically modern".[100] The recognition of H. sapiens idaltu as a valid subspecies of the anatomically modern human lineage would justify the description of contemporary humans with the subspecies name Homo sapiens sapiens.[101] However, biological anthropologist Chris Stringer does not consider idaltu distinct enough within H. sapiens to warrant its own subspecies designation.[102][33]
A further division of AMH into "early" or "robust" vs. "post-glacial" or "gracile" subtypes has since been used for convenience. The emergence of "gracile AMH" is taken to reflect a process towards a smaller and more fine-boned skeleton beginning around 50,000–30,000 years ago.[103]
Braincase anatomy
The cranium lacks a pronounced occipital bun in the neck, a bulge that anchored considerable neck muscles in Neanderthals. Modern humans, even the earlier ones, generally have a larger fore-brain than the archaic people, so that the brain sits above rather than behind the eyes. This will usually (though not always) give a higher forehead, and reduced brow ridge. Early modern people and some living people do however have quite pronounced brow ridges, but they differ from those of archaic forms by having both a supraorbital foramen or notch, forming a groove through the ridge above each eye.[104] This splits the ridge into a central part and two distal parts. In current humans, often only the central section of the ridge is preserved (if it is preserved at all). This contrasts with archaic humans, where the brow ridge is pronounced and unbroken.[105]
Modern humans commonly have a steep, even vertical forehead whereas their predecessors had foreheads that sloped strongly backwards.[106] According to Desmond Morris, the vertical forehead in humans plays an important role in human communication through eyebrow movements and forehead skin wrinkling.[107]
Brain size in both Neanderthals and AMH is significantly larger on average (but overlapping in range) than brain size in H. erectus. Neanderthal and AMH brain sizes are in the same range, but there are differences in the relative sizes of individual brain areas, with significantly larger visual systems in Neanderthals than in AMH.[108][note 11]
Jaw anatomy
Compared to archaic people, anatomically modern humans have smaller, differently shaped teeth.[111][112] This results in a smaller, more receded dentary, making the rest of the jaw-line stand out, giving an often quite prominent chin. The central part of the mandible forming the chin carries a triangularly shaped area forming the apex of the chin called the mental trigon, not found in archaic humans.[113] Particularly in living populations, the use of fire and tools requires fewer jaw muscles, giving slender, more gracile jaws. Compared to archaic people, modern humans have smaller, lower faces.
Body skeleton structure
The body skeletons of even the earliest and most robustly built modern humans were less robust than those of Neanderthals (and from what little we know from Denisovans), having essentially modern proportions. Particularly regarding the long bones of the limbs, the distal bones (the radius/ulna and tibia/fibula) are nearly the same size or slightly shorter than the proximal bones (the humerus and femur). In ancient people, particularly Neanderthals, the distal bones were shorter, usually thought to be an adaptation to cold climate.[114] The same adaptation is found in some modern people living in the polar regions.[115]
Height ranges overlap between Neanderthals and AMH, with Neanderthal averages cited as 164 to 168 cm (65 to 66 in) and 152 to 156 cm (60 to 61 in) for males and females, respectively.[note 12] By comparison, contemporary national averages range between 158 to 184 cm (62 to 72 in) in males and 147 to 172 cm (58 to 68 in) in females. Neanderthal ranges approximate the height distribution measured among Malay people, for one.[note 13]
Recent evolution
Following the peopling of Africa some 130,000 years ago, and the recent Out-of-Africa expansion some 70,000 to 50,000 years ago, some sub-populations of H. sapiens have been essentially isolated for tens of thousands of years prior to the early modern Age of Discovery. Combined with archaic admixture this has resulted in significant genetic variation, which in some instances has been shown to be the result of directional selection taking place over the past 15,000 years, i.e. significantly later than possible archaic admixture events.[118]
Some climatic adaptations, such as high-altitude adaptation in humans, are thought to have been acquired by archaic admixture. Introgression of genetic variants acquired by Neanderthal admixture have different distributions in European and East Asians, reflecting differences in recent selective pressures. A 2014 study reported that Neanderthal-derived variants found in East Asian populations showed clustering in functional groups related to immune and haematopoietic pathways, while European populations showed clustering in functional groups related to the lipid catabolic process.[note 14] A 2017 study found correlation of Neanderthal admixture in phenotypic traits in modern European populations.[120]
Physiological or phenotypical changes have been traced to Upper Paleolithic mutations, such as the East Asian variant of the EDAR gene, dated to c. 35,000 years ago.[note 15]
Recent divergence of Eurasian lineages was sped up significantly during the Last Glacial Maximum, the Mesolithic and the Neolithic, due to increased selection pressures and due to founder effects associated with migration.[123] Alleles predictive of light skin have been found in Neanderthals,[124] but the alleles for light skin in Europeans and East Asians, associated with KITLG and ASIP, are (as of 2012) thought to have not been acquired by archaic admixture but recent mutations since the LGM.[123] Phenotypes associated with the "white" or "Caucasian" populations of Western Eurasian stock emerge during the LGM, from about 19,000 years ago. Average cranial capacity in modern human populations varies in the range of 1,200 to 1,450 cm3 (adult male averages). Larger cranial volume is associated with climatic region, the largest averages being found in populations of Siberia and the Arctic.[note 16][126] Both Neanderthal and EEMH had somewhat larger cranial volumes on average than modern Europeans, suggesting the relaxation of selection pressures for larger brain volume after the end of the LGM.[125]
Examples for still later adaptations related to agriculture and animal domestication including East Asian types of ADH1B associated with rice domestication,[127] or lactase persistence,[128][129] are due to recent selection pressures.
An even more recent adaptation has been proposed for the Austronesian Sama-Bajau, developed under selection pressures associated with subsisting on freediving over the past thousand years or so.[130][131]
Behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity, involving the development of language, figurative art and early forms of religion (etc.) is taken to have arisen before 40,000 years ago, marking the beginning of the Upper Paleolithic (in African contexts also known as the Later Stone Age).[132]
There is considerable debate regarding whether the earliest anatomically modern humans behaved similarly to recent or existing humans. Behavioral modernity is taken to include fully developed language (requiring the capacity for abstract thought), artistic expression, early forms of religious behavior,[133] increased cooperation and the formation of early settlements, and the production of articulated tools from lithic cores, bone or antler. The term Upper Paleolithic is intended to cover the period since the rapid expansion of modern humans throughout Eurasia, which coincides with the first appearance of Paleolithic art such as cave paintings and the development of technological innovation such as the spear-thrower. The Upper Paleolithic begins around 50,000 to 40,000 years ago, and also coincides with the disappearance of archaic humans such as the Neanderthals.
The term "behavioral modernity" is somewhat disputed. It is most often used for the set of characteristics marking the Upper Paleolithic, but some scholars use "behavioral modernity" for the emergence of H. sapiens around 200,000 years ago,[134] while others use the term for the rapid developments occurring around 50,000 years ago.[135][136][137] It has been proposed that the emergence of behavioral modernity was a gradual process.[138][139][140][141][142]
Examples of behavioural modernity
The equivalent of the Eurasian Upper Paleolithic in African archaeology is known as the Later Stone Age, also beginning roughly 40,000 years ago. While most clear evidence for behavioral modernity uncovered from the later 19th century was from Europe, such as the Venus figurines and other artefacts from the Aurignacian, more recent archaeological research has shown that all essential elements of the kind of material culture typical of contemporary San hunter-gatherers in Southern Africa was also present by at least 40,000 years ago, including digging sticks of similar materials used today, ostrich egg shell beads, bone arrow heads with individual maker's marks etched and embedded with red ochre, and poison applicators.[144] There is also a suggestion that "pressure flaking best explains the morphology of lithic artifacts recovered from the c. 75-ka Middle Stone Age levels at Blombos Cave, South Africa. The technique was used during the final shaping of Still Bay bifacial points made on heat‐treated silcrete."[145] Both pressure flaking and heat treatment of materials were previously thought to have occurred much later in prehistory, and both indicate a behaviourally modern sophistication in the use of natural materials. Further reports of research on cave sites along the southern African coast indicate that "the debate as to when cultural and cognitive characteristics typical of modern humans first appeared" may be coming to an end, as "advanced technologies with elaborate chains of production" which "often demand high-fidelity transmission and thus language" have been found at the South African Pinnacle Point Site 5–6. These have been dated to approximately 71,000 years ago. The researchers suggest that their research "shows that microlithic technology originated early in South Africa by 71 kya, evolved over a vast time span (c. 11,000 years), and was typically coupled to complex heat treatment that persisted for nearly 100,000 years. Advanced technologies in Africa were early and enduring; a small sample of excavated sites in Africa is the best explanation for any perceived 'flickering' pattern."[146] These results suggest that Late Stone Age foragers in Sub-Saharan Africa had developed modern cognition and behaviour by at least 50,000 years ago.[147] The change in behavior has been speculated to have been a consequence of an earlier climatic change to much drier and colder conditions between 135,000 and 75,000 years ago.[148] This might have led to human groups who were seeking refuge from the inland droughts, expanded along the coastal marshes rich in shellfish and other resources. Since sea levels were low due to so much water tied up in glaciers, such marshlands would have occurred all along the southern coasts of Eurasia. The use of rafts and boats may well have facilitated exploration of offshore islands and travel along the coast, and eventually permitted expansion to New Guinea and then to Australia.[149]
In addition, a variety of other evidence of abstract imagery, widened subsistence strategies, and other "modern" behaviors has been discovered in Africa, especially South, North, and East Africa, predating 50,000 years ago. The Blombos Cave site in South Africa, for example, is famous for rectangular slabs of ochre engraved with geometric designs. Using multiple dating techniques, the site was confirmed to be around 77,000 and 100–75,000 years old.[150][151] Ostrich egg shell containers engraved with geometric designs dating to 60,000 years ago were found at Diepkloof, South Africa.[152] Beads and other personal ornamentation have been found from Morocco which might be as much as 130,000 years old; as well, the Cave of Hearths in South Africa has yielded a number of beads dating from significantly prior to 50,000 years ago,[153] and shell beads dating to about 75,000 years ago have been found at Blombos Cave, South Africa.[154][155][156] Specialized projectile weapons as well have been found at various sites in Middle Stone Age Africa, including bone and stone arrowheads at South African sites such as Sibudu Cave (along with an early bone needle also found at Sibudu) dating approximately 60,000-70,000 years ago,[157][158][159][160][161] and bone harpoons at the Central African site of Katanda dating ca. 90,000 years ago.[162] Evidence also exists for the systematic heat treating of silcrete stone to increased its flake-ability for the purpose of toolmaking, beginning approximately 164,000 years ago at the South African site of Pinnacle Point and becoming common there for the creation of microlithic tools at about 72,000 years ago.[163][146]
In 2008, an ochre processing workshop likely for the production of paints was uncovered dating to ca. 100,000 years ago at Blombos Cave, South Africa. Analysis shows that a liquefied pigment-rich mixture was produced and stored in the two abalone shells, and that ochre, bone, charcoal, grindstones and hammer-stones also formed a composite part of the toolkits. Evidence for the complexity of the task includes procuring and combining raw materials from various sources (implying they had a mental template of the process they would follow), possibly using pyrotechnology to facilitate fat extraction from bone, using a probable recipe to produce the compound, and the use of shell containers for mixing and storage for later use.[164][165][166] Modern behaviors, such as the making of shell beads, bone tools and arrows, and the use of ochre pigment, are evident at a Kenyan site by 78,000-67,000 years ago.[167] Evidence of early stone-tipped projectile weapons (a characteristic tool of Homo sapiens), the stone tips of javelins or throwing spears, were discovered in 2013 at the Ethiopian site of Gademotta, and date to around 279,000 years ago.[168]
Expanding subsistence strategies beyond big-game hunting and the consequential diversity in tool types has been noted as signs of behavioral modernity. A number of South African sites have shown an early reliance on aquatic resources from fish to shellfish. Pinnacle Point, in particular, shows exploitation of marine resources as early as 120,000 years ago, perhaps in response to more arid conditions inland.[169] Establishing a reliance on predictable shellfish deposits, for example, could reduce mobility and facilitate complex social systems and symbolic behavior. Blombos Cave and Site 440 in Sudan both show evidence of fishing as well. Taphonomic change in fish skeletons from Blombos Cave have been interpreted as capture of live fish, clearly an intentional human behavior.[153]
Humans in North Africa (Nazlet Sabaha, Egypt) are known to have dabbled in chert mining, as early as ≈100,000 years ago, for the construction of stone tools.[170][171]
Evidence was found in 2018, dating to about 320,000 years ago at the site of Olorgesailie in Kenya, of the early emergence of modern behaviors including: the trade and long-distance transportation of resources (such as obsidian), the use of pigments, and the possible making of projectile points. The authors of three 2018 studies on the site observe that the evidence of these behaviors is roughly contemporary with the earliest known Homo sapiens fossil remains from Africa (such as at Jebel Irhoud and Florisbad), and they suggest that complex and modern behaviors began in Africa around the time of the emergence of Homo sapiens.[172][173][174]
In 2019, further evidence of Middle Stone Age complex projectile weapons in Africa was found at Aduma, Ethiopia, dated 100,000-80,000 years ago, in the form of points considered likely to belong to darts delivered by spear throwers.[175]
Pace of progress during Homo sapiens history
Homo sapiens technological and cultural progress appears to have been very much faster in recent millennia than in Homo sapiens early periods. The pace of development may indeed have accelerated, due to massively larger population (so more humans extant to think of innovations), more communication and sharing of ideas among human populations, and the accumulation of thinking tools. However it may also be that the pace of advance always looks relatively faster to humans in the time they live, because previous advances are unrecognised 'givens'.[176][177]
Notes
- ^ a b Based on Schlebusch et al., "Southern African ancient genomes estimate modern human divergence to 350,000 to 260,000 years ago",[7] Fig. 3 (H. sapiens divergence times) and Stringer (2012),[8] (archaic admixture).
- ^ This is a matter of convention (rather than a factual dispute), and there is no universal consensus on terminology. Some scholars include humans of up to 600,000 years ago under the same species. See Bryant (2003), p. 811.[14] See also Tattersall (2012), Page 82 (cf. Unfortunately this consensus in principle hardly clarifies matters much in practice. For there is no agreement on what the 'qualities of a man' actually are," [...]).[15]
- ^ Werdelin[16] citing Lieberman et al.[17]
- ^ The history of claimed or proposed subspecies of H. sapiens is complicated and fraught with controversy. The only widely recognized archaic subspecies[citation needed] is H. sapiens idaltu (2003). The name H. s. sapiens is due to Linnaeus (1758), and refers by definition the subspecies of which Linnaeus himself is the type specimen. However, Linnaeus postulated four other extant subspecies, viz. H. s. afer, H. s. americanus, H. s. asiaticus and H. s. ferusfor Africans, Americans, Asians and Malay. This classification remained in common usage until the mid 20th century, sometimes alongside H. s. tasmanianus for Australians. See, for example, Bailey, 1946;[21] Hall, 1946.[22] The division of extant human populations into taxonomic subspecies was gradually given up in the 1970s (for example, Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia[23]).
- ^ Homo sapiens sapiens is first used in the 1940s as a synonym of Linnaeus' H. s. europaeus, i. e. Caucasoids.[22] This usage is abandoned by the 1970s, and H. s. sapienswas now used for Cro-Magnon by authors who wished to classify Neanderthals as subspecies of H. sapiens taken in a wider sense, for example Seely.[27]
- ^ For example, "DMA studies have revealed that the first anatomically modern humans (H. s. sapiens) arose in Africa between 200,000 and 140,000 years ago".[28] This usage persists alongside H. s. sapiens designating Upper Paleolithic Cro Magnon, for example. "About 200,000 years ago our own species, Homo sapiens (the thinking human), evolved [...] About 60,000 years ago we became elaborate artisans, building boats and intricate shelters; at this stage, scientists refer to us as Homo sapiens sapiens."[29]
- ^ (95% confidence interval 237–581 kya)[63]
- ^ "Although none of the Qesem teeth shows a suite of Neanderthal characters, a few traits may suggest some affinities with members of the Neanderthal evolutionary lineage. However, the balance of the evidence suggests a closer similarity with the Skhul/Qafzeh dental material, although many of these resemblances likely represent plesiomorphous features."[67]
- ^ "Currently available genetic and archaeological evidence is generally interpreted as supportive of a recent single origin of modern humans in East Africa."[88]
- ^ It is important to note that this is a question of conventional terminology, not one of a factual disagreement. Pääbo (2014) frames this as a debate that is unresolvable in principle, "since there is no definition of species perfectly describing the case."[99]
- ^ Contemporary human endocranial volume averages at 1,350 cm3 (82 cu in), with significant differences between populations, global group means range 1,085–1,580 cm3(66.2–96.4 cu in).[109] Neanderthal average is close to 1,450 cm3 (88 cu in) (male average 1,600 cm3 (98 cu in), female average 1,300 cm3 (79 cu in)), with a range extending up to 1,736 cm3 (105.9 cu in) (Amud 1).[110]
- ^ "Based on 45 long bones from maximally 14 males and 7 females, Neanderthals' height averages between 164 and 168 (males) resp. 152 to 156 cm (females). This height is indeed 12-14 cm lower than the height of post-WWII Europeans, but compared to Europeans some 20,000 or 100 years ago, it is practically identical or even slightly higher."[116]
- ^ Malay, 20–24 (N= m:749 f:893, Median= m:166 cm (5 ft 51⁄2 in) f:155 cm (5 ft 1 in), SD= m:6.46 cm (21⁄2 in) f:6.04 cm (21⁄2 in))[117]
- ^ "Specifically, genes in the LCP [lipid catabolic process] term had the greatest excess of NLS in populations of European descent, with an average NLS frequency of 20.8±2.6% versus 5.9±0.08% genome wide (two-sided t-test, P<0.0001, n=379 Europeans and n=246 Africans). Further, among examined out-of-Africa human populations, the excess of NLS [Neanderthal-like genomic sites] in LCP genes was only observed in individuals of European descent: the average NLS frequency in Asians is 6.7±0.7% in LCP genes versus 6.2±0.06% genome wide."[119]
- ^ Traits affected by the mutation are sweat glands, teeth, hair thickness and breast tissue.[121][122]
- ^ "We offer an alternative hypothesis that suggests that hominid expansion into regions of cold climate produced change in head shape. Such change in shape contributed to the increased cranial volume. Bioclimatic effects directly upon body size (and indirectly upon brain size) in combination with cranial globularity appear to be a fairly powerful explanation of ethnic group differences." (figure in Beals, p304)[125]
References
- ^ Global Mammal Assessment Team (2008). "Homo sapiens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T136584A4313662. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T136584A4313662.en.
- ^ a b Tomkins, Stephen. 1998. The Origins of Humankind (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p 107.
- ^ a b Barnes-Svarney, Patricia, and Thomas E. Svarney. 1999. The Oryx Guide to Natural History: The Earth and All Its Inhabitants. Phoenix, AZ: Oryx Press. indexing "sapiens sapiens".
- ^ a b Bánáthy, Béla H. 2000. Guided Evolution of Society: A Systems View. New York: Springer Science+Business Media. indexing "sapiens sapiens".
- ^ a b c d e f Mounier, Aurélien; Lahr, Marta (2019). "Deciphering African late middle Pleistocene hominin diversity and the origin of our species". Nature Communications. 10(1): 3406. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.3406M. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11213-w. PMC 6736881. PMID 31506422.
- ^ a b Scerri, Eleanor M. L.; Thomas, Mark G.; Manica, Andrea; Gunz, Philipp; Stock, Jay T.; Stringer, Chris; Grove, Matt; Groucutt, Huw S.; Timmermann, Axel; Rightmire, G. Philip; d’Errico, Francesco (2018-08-01). "Did Our Species Evolve in Subdivided Populations across Africa, and Why Does It Matter?". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 33 (8): 582–594. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2018.05.005. ISSN 0169-5347. PMC 6092560. PMID 30007846.
- ^ a b Schlebusch; et al. (3 November 2017). "Southern African ancient genomes estimate modern human divergence to 350,000 to 260,000 years ago". Science. 358 (6363): 652–655. Bibcode:2017Sci...358..652S. doi:10.1126/science.aao6266. PMID 28971970.
- ^ a b Stringer, C (2012). "What makes a modern human". Nature. 485 (7396): 33–35. Bibcode:2012Natur.485...33S. doi:10.1038/485033a. PMID 22552077.
- ^ a b Neubauer, Simon; Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Gunz, Philipp (2018-01-01). "The evolution of modern human brain shape". Science Advances. 4 (1): eaao5961. Bibcode:2018SciA....4.5961N. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aao5961. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 5783678. PMID 29376123.
- ^ Harrod, James. "Harrod (2014) Suppl File Table 1 mtDNA language myth Database rev May 17 2019.doc". Mother Tongue.
- ^ Nitecki, Matthew H; Nitecki, Doris V (1994). Origins of Anatomically Modern Humans. Springer. ISBN 1489915079.
- ^ Hammond, Ashley S.; Royer, Danielle F.; Fleagle, John G. (Jul 2017). "The Omo-Kibish I pelvis". Journal of Human Evolution. 108: 199–219. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.04.004. ISSN 1095-8606. PMID 28552208.
- ^ Linné, Carl von (1758). Systema naturæ. Regnum animale (10th ed.). Sumptibus Guilielmi Engelmann. pp. 18, 20. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Bryant, Clifton D (2003). Handbook of Death and Dying. SAGE. ISBN 0761925147.
- ^ Tattersall, Ian (2012). Masters of the Planet: The Search for Our Human Origins. St Martin's Press. ISBN 978-1137000385.
- ^ Werdelin, Lars; Sanders, William Joseph (2010). Cenozoic Mammals of Africa. Univ of California Press. p. 517. ISBN 9780520257214.
- ^ Lieberman, DE; McBratney, BM; Krovitz, G (2002). "The evolution and development of cranial form in Homo sapiens". PNAS. 99 (3): 1134–39. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.1134L. doi:10.1073/pnas.022440799. PMC 122156. PMID 11805284.
- ^ Hajdinjak, Mateja; Fu, Qiaomei; Hübner, Alexander; Petr, Martin; et al. (2018-03-01). "Reconstructing the genetic history of late Neanderthals". Nature. 555 (7698): 652–656. Bibcode:2018Natur.555..652H. doi:10.1038/nature26151. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 6485383. PMID 29562232.
- ^ Meyer, Matthias; Arsuaga, Juan-Luis; de Filippo, Cesare; Nagel, Sarah; et al. (2016-03-01). "Nuclear DNA sequences from the Middle Pleistocene Sima de los Huesos hominins". Nature. 531 (7595): 504–507. Bibcode:2016Natur.531..504M. doi:10.1038/nature17405. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 26976447.
- ^ Gómez-Robles, Aida (2019-05-01). "Dental evolutionary rates and its implications for the Neanderthal–modern human divergence". Science Advances. 5 (5): –1268. Bibcode:2019SciA....5.1268G. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw1268. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 6520022. PMID 31106274.
- ^ Bailey, John Wendell (1946). The Mammals of Virginia. p. 356.
- ^ a b Hall, E (1946). "Zoological Subspecies of Man at the Peace Table". Journal of Mammalogy. 27 (4): 358–364. doi:10.2307/1375342. JSTOR 1375342.
- ^ Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. 11. 1970. p. 55.
- ^ Hublin, J. J. (2009). "The origin of Neandertals". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (38): 16022–27. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10616022H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904119106. JSTOR 40485013. PMC 2752594. PMID 19805257.
- ^ Harvati, K.; Frost, S.R.; McNulty, K.P. (2004). "Neanderthal taxonomy reconsidered: implications of 3D primate models of intra- and interspecific differences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (5): 1147–52. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.1147H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308085100. PMC 337021. PMID 14745010.
- ^ "Homo neanderthalensis King, 1864". Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Human Evolution. Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell. 2013. pp. 328–31.
- ^ Seely, Paul H (1971). "Not a Viable Theory". The Journal of the American Scientific Affiliation. 23 (4): 134.
- ^ Parker, Geoffrey (2001). Compact history of the world. p. 14. ISBN 9780760725757.
- ^ Rosenstand, Nina (2002). The Human Condition: An Introduction to Philosophy of Human Nature. McGraw-Hill. p. 42. ISBN 1559347643.
- ^ Schlebusch, Carina M.; Malmström, Helena; Günther, Torsten; Sjödin, Per; Coutinho, Alexandra; Edlund, Hanna; Munters, Arielle R.; Steyn, Maryna; Soodyall, Himla; Lombard, Marlize; Jakobsson, Mattias (5 June 2017). "Ancient genomes from southern Africa pushes modern human divergence beyond 260,000 years ago". bioRxiv 10.1101/145409.
- ^ Schlebusch, Carina M.; Malmström, Helena; Günther, Torsten; Sjödin, Per; Coutinho, Alexandra; Edlund, Hanna; Munters, Arielle R.; Vicente, Mário; Steyn, Maryna; Soodyall, Himla; Lombard, Marlize (2017-11-03). "Southern African ancient genomes estimate modern human divergence to 350,000 to 260,000 years ago". Science. 358 (6363): 652–655. Bibcode:2017Sci...358..652S. doi:10.1126/science.aao6266. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 28971970.
- ^ a b c Callaway, Ewan (7 June 2017). "Oldest Homo sapiens fossil claim rewrites our species' history". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2017.22114. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Stringer, C. (2016). "The origin and evolution of Homo sapiens". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 371 (1698): 20150237. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0237. PMC 4920294. PMID 27298468.
- ^ a b Sample, Ian (7 June 2017). "Oldest Homo sapiens bones ever found shake foundations of the human story". The Guardian. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ a b Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Ben-Ncer, Abdelouahed; Bailey, Shara E.; Freidline, Sarah E.; Neubauer, Simon; Skinner, Matthew M.; Bergmann, Inga; Le Cabec, Adeline; Benazzi, Stefano; Harvati, Katerina; Gunz, Philipp (2017). "New fossils from Jebel Irhoud, Morocco and the pan-African origin of Homo sapiens" (PDF). Nature. 546 (7657): 289–292. Bibcode:2017Natur.546..289H. doi:10.1038/nature22336. PMID 28593953.
- ^ a b Scerri, M.L.; et al. (2018). "Did Our Species Evolve in Subdivided Populations across Africa, and Why Does It Matter?". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 33 (8): 582–594. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2018.05.005. PMC 6092560. PMID 30007846.
- ^ Chan, Eva, K. F.; et al. (28 October 2019). "Human origins in a southern African palaeo-wetland and first migrations". Nature. 857 (7781): 185–189. Bibcode:2019Natur.575..185C. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1714-1. PMID 31659339.
- ^ Sample, Ian (28 October 2019). "Ancestral home of modern humans is in Botswana, study finds". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 29 October 2019.
- ^ Woodward, Aylin (28 October 2019). "New Study Pinpoints The Ancestral Homeland of All Humans Alive Today". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 29 October 2019.
- ^ a b Yong, Ed (28 October 2019). "Has Humanity's Homeland Been Found?". The Atlantic. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ^ a b c Zimmer, Carl (10 September 2019). "Scientists Find the Skull of Humanity's Ancestor — on a Computer - By comparing fossils and CT scans, researchers say they have reconstructed the skull of the last common forebear of modern humans". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 September 2019.
- ^ Rogers, Alan R.; Bohlender, Ryan J.; Huff, Chad D. (12 September 2017). "Early history of Neanderthals and Denisovans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114(37): 9859–9863. doi:10.1073/pnas.1706426114. PMC 5604018. PMID 28784789.
- ^ Wolpoff, M. H.; Spuhler, J. N.; Smith, F. H.; Radovcic, J.; Pope, G.; Frayer, D. W.; Eckhardt, R.; Clark, G. (1988). "Modern Human Origins". Science. 241 (4867): 772–74. Bibcode:1988Sci...241..772W. doi:10.1126/science.3136545. PMID 3136545.
- ^ a b c Green RE, Krause J, Briggs AW, Maricic T, Stenzel U, Kircher M, Patterson N, Li H, Zhai W, Fritz MH, Hansen NF, Durand EY, Malaspinas A, Jensen JD, Marques-Bonet T, Alkan C, Prüfer K, Meyer M, Burbano HA, Good JM, Schultz R, Aximu-Petri A, Butthof A, Höber B, Höffner B, Siegemund M, Weihmann A, Nusbaum C, Lander ES, et al. (May 2010). "A draft sequence of the Neandertal genome". Science. 328 (5979): 710–22. Bibcode:2010Sci...328..710G. doi:10.1126/science.1188021. PMC 5100745. PMID 20448178.
- ^ Reich D, Patterson N, Kircher M, Delfin F, Nandineni MR, Pugach I, Ko AM, Ko Y, Jinam TA, Phipps ME, Saitou N, Wollstein A, Kayser M, Pääbo S, Stoneking M (2011). "Denisova admixture and the first modern human dispersals into southeast Asia and oceania". Am J Hum Genet. 89 (4): 516–28. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.09.005. PMC 3188841. PMID 21944045.
- ^ "New Clues Add 40,000 Years to Age of Human Species". www.nsf.gov. NSF – National Science Foundation.
- ^ "Age of ancient humans reassessed". BBC News. February 16, 2005. Retrieved April 10, 2010.
- ^ "The Oldest Homo Sapiens: Fossils Push Human Emergence Back To 195,000 Years Ago". ScienceDaily. February 28, 2005. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Alemseged, Z.; Coppens, Y.; Geraads, D. (2002). "Hominid cranium from Homo: Description and taxonomy of Homo-323-1976-896". Am J Phys Anthropol. 117 (2): 103–12. doi:10.1002/ajpa.10032. PMID 11815945.
- ^ Stoneking, Mark; Soodyall, Himla (1996). "Human evolution and the mitochondrial genome". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 6 (6): 731–36. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(96)80028-1. PMID 8994844.
- ^ Human evolution: the fossil evidence in 3D, by Philip L. Walker and Edward H. Hagen, Dept. of Anthropology, University of California, Santa Barbara. Retrieved April 5, 2005.
- ^ Meyer, Matthias; Arsuaga, Juan-Luis; de Filippo, Cesare; Nagel, Sarah; Aximu-Petri, Ayinuer; Nickel, Birgit; Martínez, Ignacio; Gracia, Ana; de Castro, José María Bermúdez; Carbonell, Eudald; Viola, Bence; Kelso, Janet; Prüfer, Kay; Pääbo, Svante (14 March 2016). "Nuclear DNA sequences from the Middle Pleistocene Sima de los Huesos hominins". Nature. 531 (7595): 504–507. Bibcode:2016Natur.531..504M. doi:10.1038/nature17405. PMID 26976447.
- ^ Callaway, Ewen (14 March 2016). "Oldest ancient-human DNA details dawn of Neanderthals". Nature. 531 (7594): 296–286. Bibcode:2016Natur.531..296C. doi:10.1038/531286a. PMID 26983523.
- ^ Oppenheimer, S. (2003). Out of Eden: The Peopling of the World. ISBN 978-1-84119-697-8.
- ^ Trinkaus, E.; Moldovan, O.; Milota, Ș.; Bîlgăr, A.; Sarcina, L.; Athreya, S.; Bailey, S. E.; Rodrigo, R.; et al. (2003). "An early modern human from Peștera cu Oase, Romania". PNAS. 100 (20): 11231–36. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10011231T. doi:10.1073/pnas.2035108100. PMC 208740. PMID 14504393.
- ^ a b Reich, David; Green, Richard E.; Kircher, Martin; Krause, Johannes; Patterson, Nick; Durand, Eric Y.; Viola, Bence; Briggs, Adrian W.; et al. (2010). "Genetic history of an archaic hominin group from Denisova Cave in Siberia". Nature. 468 (7327): 1053–60. Bibcode:2010Natur.468.1053R. doi:10.1038/nature09710. hdl:10230/25596. PMC 4306417. PMID 21179161.
- ^ Trinkaus, Erik (October 2005). "Early modern humans". Annual Review of Anthropology. 34 (1): 207–30. doi:10.1146/annurev.anthro.34.030905.154913. S2CID 9039428.
- ^ Meldrum, Jeff; Hilton, Charles E. (31 March 2004). From Biped to Strider: The Emergence of Modern Human Walking, Running, and Resource Transport. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-0-306-48000-3.
- ^ Vonk, Jennifer; Shackelford, Todd K. (13 February 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Comparative Evolutionary Psychology. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 429–. ISBN 978-0-19-973818-2.
- ^ Bozek, Katarzyna; Wei, Yuning; Yan, Zheng; Liu, Xiling; Xiong, Jieyi; Sugimoto, Masahiro; Tomita, Masaru; Pääbo, Svante; Pieszek, Raik; Sherwood, Chet C.; Hof, Patrick R.; Ely, John J.; Steinhauser, Dirk; Willmitzer, Lothar; Bangsbo, Jens; Hansson, Ola; Call, Josep; Giavalisco, Patrick; Khaitovich, Philipp (2014). "Exceptional Evolutionary Divergence of Human Muscle and Brain Metabolomes Parallels Human Cognitive and Physical Uniqueness". PLOS Biology. 12 (5): e1001871. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001871. PMC 4035273. PMID 24866127.
- ^ Thieme, H (2007). "Der große Wurf von Schöningen: Das neue Bild zur Kultur des frühen Menschen". Die Schöninger Speere – Mensch und Jagd vor 400 000 Jahren. Konrad Theiss Verlag. pp. 224–28. ISBN 978-3-89646-040-0.
- ^ Haidle, M.N. (2006). "Menschenaffen? Affenmenschen? Mensch! Kognition und Sprache im Altpaläolithikum". In Conard, N.J. (ed.). Woher kommt der Mensch. Attempto Verlag. pp. 69–97. ISBN 3-89308-381-2.
- ^ Mendez, Fernando; Krahn, Thomas; Schrack, Bonnie; Krahn, Astrid-Maria; Veeramah, Krishna; Woerner, August; Fomine, Forka Leypey Mathew; Bradman, Neil; Thomas, Mark (7 March 2013). "An African American paternal lineage adds an extremely ancient root to the human Y chromosome phylogenetic tree" (PDF). American Journal of Human Genetics. 92 (3): 454–59. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.02.002. PMC 3591855. PMID 23453668.
- ^ Krings M, Stone A, Schmitz RW, Krainitzki H, Stoneking M, Pääbo S (July 1997). "Neandertal DNA sequences and the origin of modern humans". Cell. 90 (1): 19–30. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80310-4. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0025-0960-8. PMID 9230299.
- ^ Hill, Deborah (16 March 2004). "No Neandertals in the Gene Pool". Science. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Serre, D; Langaney, A; Chech, M; Teschler-Nicola, M; Paunovic, M; Mennecier, P; Hofreiter, M; Possnert, G; Pääbo, S (2004). "No evidence of Neandertal mtDNA contribution to early modern humans". PLOS Biology. 2 (3): 313–17. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020057. PMC 368159. PMID 15024415.
- ^ Hershkovitz, I; Smith, P; Sarig, R; Quam, R; Rodríguez, L; García, R; Arsuaga, JL; Barkai, R; Gopher, A (2011). "Middle pleistocene dental remains from Qesem Cave (Israel)". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 144 (4): 575–592. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21446. PMID 21404234. S2CID 3106938.
- ^ Posth, Cosimo; et al. (4 July 2017). "Deeply divergent archaic mitochondrial genome provides lower time boundary for African gene flow into Neanderthals". Nature Communications. 8: 16046. Bibcode:2017NatCo...816046P. doi:10.1038/ncomms16046. PMC 5500885. PMID 28675384.
- ^ White, Tim D.; Asfaw, Berhane; Degusta, David; Gilbert, Henry; Richards, Gary D.; Suwa, Gen; Howell, Clark F. (June 2003). "Pleistocene Homo sapiens from Middle Awash, Ethiopia". Nature. 423 (6941): 742–7. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..742W. doi:10.1038/nature01669. PMID 12802332.
- ^ "Fossil Reanalysis Pushes Back Origin of Homo sapiens". Scientific American. 2005-02-17. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Mehta, Ankita (26 January 2018). "A 177,000-year-old jawbone fossil discovered in Israel is oldest human remains found outside Africa". International Business Times. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Bae, Christopher J.; Douka, Katerina; Petraglia, Michael D. (8 December 2017). "On the origin of modern humans: Asian perspectives". Science. 358 (6368): eaai9067. doi:10.1126/science.aai9067. PMID 29217544.
- ^ Kuo, Lily (10 December 2017). "Early humans migrated out of Africa much earlier than we thought". Quartz. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (10 July 2019). "A Skull Bone Discovered in Greece May Alter the Story of Human Prehistory - The bone, found in a cave, is the oldest modern human fossil ever discovered in Europe. It hints that humans began leaving Africa far earlier than once thought". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ Staff (10 July 2019). "'Oldest remains' outside Africa reset human migration clock". Phys.org. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ Harvati, Katerina; et al. (10 July 2019). "Apidima Cave fossils provide earliest evidence of Homo sapiens in Eurasia". Nature. 571 (7766): 500–504. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1376-z. PMID 31292546.
- ^ Rito, T; Richards, MB; Fernandes, V; Alshamali, F; Cerny, V; Pereira, L; Soares, P (2013). "The first modern human dispersals across Africa". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e80031. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880031R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080031. PMC 3827445. PMID 24236171.
- ^ Henn, Brenna; Gignoux, Christopher R.; Jobin, Matthew (2011). "Hunter-gatherer genomic diversity suggests a southern African origin for modern humans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (13): 5154–62. Bibcode:2011PNAS..108.5154H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1017511108. PMC 3069156. PMID 21383195.
- ^ a b c Higham, Thomas F. G.; Wesselingh, Frank P.; Hedges, Robert E. M.; Bergman, Christopher A.; Douka, Katerina (2013-09-11). "Chronology of Ksar Akil (Lebanon) and Implications for the Colonization of Europe by Anatomically Modern Humans". PLOS ONE. 8 (9): e72931. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...872931D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072931. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3770606. PMID 24039825.
- ^ Posth C, Renaud G, Mittnik M, Drucker DG, Rougier H, Cupillard C, Valentin F, Thevenet C, Furtwängler A, Wißing C, Francken M, Malina M, Bolus M, Lari M, Gigli E, Capecchi G, Crevecoeur I, Beauval C, Flas D, Germonpré M, van der Plicht J, Cottiaux R, Gély B, Ronchitelli A, Wehrberger K, Grigorescu D, Svoboda J, Semal P, Caramelli D, Bocherens H, Harvati K, Conard NJ, Haak W, Powell A, Krause J (2016). "Pleistocene Mitochondrial Genomes Suggest a Single Major Dispersal of Non-Africans and a Late Glacial Population Turnover in Europe". Current Biology. 26 (6): 827–833. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.037. hdl:2440/114930. PMID 26853362.
- ^ Kamin M, Saag L, Vincente M, et al. (April 2015). "A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture". Genome Research. 25 (4): 459–466. doi:10.1101/gr.186684.114. PMC 4381518. PMID 25770088.
- ^ Vai S, Sarno S, Lari M, Luiselli D, Manzi G, Gallinaro M, Mataich S, Hübner A, Modi A, Pilli E, Tafuri MA, Caramelli D, di Lernia S (March 2019). "Ancestral mitochondrial N lineage from the Neolithic 'green' Sahara". Sci Rep. 9 (1): 3530. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.3530V. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39802-1. PMC 6401177. PMID 30837540.
- ^ a b Haber M, Jones AL, Connel BA, Asan, Arciero E, Huanming Y, Thomas MG, Xue Y, Tyler-Smith C (June 2019). "A Rare Deep-Rooting D0 African Y-chromosomal Haplogroup and its Implications for the Expansion of Modern Humans Out of Africa". Genetics. 212(4): 1421–1428. doi:10.1534/genetics.119.302368. PMC 6707464. PMID 31196864.
- ^ Clarkson, Chris; Jacobs, Zenobia; Pardoe, Colin (2017). "Human occupation of northern Australia by 65,000 years ago" (PDF). Nature. 547 (7663): 306–310. Bibcode:2017Natur.547..306C. doi:10.1038/nature22968. hdl:2440/107043. PMID 28726833.
- ^ St. Fleu, Nicholas (July 19, 2017). "Humans First Arrived in Australia 65,000 Years Ago, Study Suggests". New York Times.
- ^ Wood R (2017-09-02). "Comments on the chronology of Madjedbebe". Australian Archaeology. 83 (3): 172–174. doi:10.1080/03122417.2017.1408545. ISSN 0312-2417.
- ^ O'Connell JF, Allen J, Williams MA, Williams AN, Turney CS, Spooner NA, et al. (August 2018). "Homo sapiens first reach Southeast Asia and Sahul?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (34): 8482–8490. doi:10.1073/pnas.1808385115. PMC 6112744. PMID 30082377.
- ^ Liu, Hua; et al. (2006). "A Geographically Explicit Genetic Model of Worldwide Human-Settlement History". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 79 (2): 230–237. doi:10.1086/505436. PMC 1559480. PMID 16826514.
- ^ "Out of Africa Revisited". Science. 308 (5724): 921g. 2005-05-13. doi:10.1126/science.308.5724.921g.
- ^ Sankararaman, Sriram; Mallick, Swapan; Patterson, Nick; Reich, David (2016). "The Combined Landscape of Denisovan and Neanderthal Ancestry in Present-Day Humans". Current Biology. 26 (9): 1241–47. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.037. ISSN 0960-9822. PMC 4864120. PMID 27032491.
- ^ Sánchez-Quinto, F; Botigué, LR; Civit, S; Arenas, C; Avila-Arcos, MC; Bustamante, CD; Comas, D; Lalueza-Fox, C (October 17, 2012). "North African Populations Carry the Signature of Admixture with Neandertals". PLOS ONE. 7 (10): e47765. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...747765S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047765. PMC 3474783. PMID 23082212.
- ^ Fu, Q; Li, H; Moorjani, P; Jay, F; Slepchenko, SM; Bondarev, AA; Johnson, PL; Aximu-Petri, A; Prüfer, K; de Filippo, C; Meyer, M; Zwyns, N; Salazar-García, DC; Kuzmin, YV; Keates, SG; Kosintsev, PA; Razhev, DI; Richards, MP; Peristov, NV; Lachmann, M; Douka, K; Higham, TF; Slatkin, M; Hublin, JJ; Reich, D; Kelso, J; Viola, TB; Pääbo, S (October 23, 2014). "Genome sequence of a 45,000-year-old modern human from western Siberia". Nature. 514 (7523): 445–49. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..445F. doi:10.1038/nature13810. PMC 4753769. PMID 25341783.
- ^ Brahic, Catherine (February 3, 2014). "Humanity's forgotten return to Africa revealed in DNA". The New Scientist. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ Kuhlwilm, Martin (17 February 2016). "Ancient gene flow from early modern humans into Eastern Neanderthals". Nature. 530 (7591): 429–433. Bibcode:2016Natur.530..429K. doi:10.1038/nature16544. PMC 4933530. PMID 26886800.
- ^ Ding, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, L. (2014) [Online 2013]. "Neanderthal Introgression at Chromosome 3p21.31 was Under Positive Natural Selection in East Asians". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 31 (3): 683–695. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst260. PMID 24336922.
- ^ Vernot, B.; Akey, J. M. (2014). "Resurrecting Surviving Neandertal Lineages from Modern Human Genomes". Science. 343 (6174): 1017–1021. Bibcode:2014Sci...343.1017V. doi:10.1126/science.1245938. PMID 24476670.
- ^ Ayala, Francisco José; Conde, Camilo José Cela (2017). Processes in Human Evolution: The Journey from Early Hominins to Neanderthals and Modern Humans. ISBN 9780198739906.
- ^ Schopf, J. William (1992). Major Events in the History of Life. Jones & Bartlett Learning. pp. 168–. ISBN 978-0-86720-268-7.
- ^ Pääbo, Svante (2014). Neanderthal Man: In Search of Lost Genomes. New York: Basic Books. p. 237.
- ^ Sanders, Robert (11 June 2003). "160,000-year-old fossilized skulls uncovered in Ethiopia are oldest anatomically modern humans". UC Berkeley News. Retrieved 2019-05-07.
- ^ White, Tim D.; Asfaw, B.; DeGusta, D.; Gilbert, H.; Richards, G. D.; Suwa, G.; Howell, F. C. (2003). "Pleistocene Homo sapiens from Middle Awash, Ethiopia". Nature. 423 (6491): 742–47. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..742W. doi:10.1038/nature01669. PMID 12802332.
- ^ Stringer, Chris (June 12, 2003). "Human evolution: Out of Ethiopia". Nature. 423 (6941): 693–695. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..692S. doi:10.1038/423692a. PMID 12802315.
- ^ Hawks, J.; Wang, E. T.; Cochran, G. M.; Harpending, H. C.; Moyzis, R. K. (2007). "Recent acceleration of human adaptive evolution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (52): 20753–8. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10420753H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707650104. PMC 2410101. PMID 18087044.
- ^ Bhupendra, P. (April 2019). "Forehead Anatomy". Medscape references. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ "How to ID a modern human?". News, 2012. Natural History Museum, London. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ^ "Encarta, Human Evolution". Encarta. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009.
- ^ Morris, Desmond (2007). "The Brow". The Naked Woman: A Study of the Female Body. ISBN 978-0-312-33853-4.
- ^ Pearce, Eiluned; Stringer, Chris; Dunbar, R. I. M. (2013-05-07). "New insights into differences in brain organization between Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences. 280 (1758): 20130168. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.0168. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 3619466. PMID 23486442.
- ^ Smith, C. L.; Beals, K. L. (1990). "Cultural correlates with cranial capacity". American Anthropologist. 92: 193–200. doi:10.1525/aa.1990.92.1.02a00150. S2CID 162406199.
- ^ Stringer, C (1984). "Human evolution and biological adaptation in the Pleistocene". In Foley, R (ed.). Hominid evolution and community ecology. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0122619205.
- ^ Townsend G, Richards L, Hughes T (May 2003). "Molar intercuspal dimensions: genetic input to phenotypic variation". Journal of Dental Research. 82 (5): 350–5. doi:10.1177/154405910308200505. PMID 12709500.
- ^ Keith A (1913). "Problems relating to the Teeth of the Earlier Forms of Prehistoric Man". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 6 (Odontol Sect): 103–124. doi:10.1177/003591571300601018. PMC 2005996. PMID 19977113.
- ^ Tattersall, Jeffrey H; Schwartz, Ian (2003). The human fossil record Craniodental Morphology of Genus Homo (Africa and Asia) (vol 2). Wiley-Liss. pp. 327–328. ISBN 978-0471319283.
- ^ Steegmann, A. Theodore; Cerny, Frank J.; Holliday, Trenton W. (2002). "Neandertal cold adaptation: Physiological and energetic factors". American Journal of Human Biology. 14(5): 566–583. doi:10.1002/ajhb.10070. PMID 12203812.
- ^ Stock, J.T. (October 2006). "Hunter-gatherer postcranial robusticity relative to patterns of mobility, climatic adaptation, and selection for tissue economy". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 131 (2): 194–204. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20398. PMID 16596600.
- ^ Helmuth H (1998). "Body height, body mass and surface area of the Neanderthals". Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Anthropologie. 82 (1): 1–12. PMID 9850627.
- ^ Lim TO, Ding LM, Zaki M, et al. (March 2000). "Distribution of Body Weight, Height and Body Mass Index in a National Sample of Malaysian Adults" (PDF). Med. J. Malaysia. 55(1): 108–28. PMID 11072496.
- ^ Wade, N (2006-03-07). "Still Evolving, Human Genes Tell New Story". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-07-10.
- ^ Khrameeva, E; Bozek, K; He, L; Yan, Z; Jiang, X; Wei, Y; Tang, K; Gelfand, MS; Prüfer, K; Kelso, J; Pääbo, S; Giavalisco, P; Lachmann, M; Khaitovich, P (2014). "Neanderthal ancestry drives evolution of lipid catabolism in contemporary Europeans". Nature Communications. 5 (3584): 3584. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5E3584K. doi:10.1038/ncomms4584. PMC 3988804. PMID 24690587.
- ^ Michael Dannemann 1 and Janet Kelso, "The Contribution of Neanderthals to Phenotypic Variation in Modern Humans", The American Journal of Human Genetics 101, 578–589, October 5, 2017.
- ^ Kamberov, Yana G (14 February 2013). "Modeling Recent Human Evolution in Mice by Expression of a Selected EDAR Variant". Cell. 152 (4): 691–702. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.016. PMC 3575602. PMID 23415220.
- ^ Wade, Nicholas (14 February 2013). "East Asian Physical Traits Linked to 35,000-Year-Old Mutation". The New York Times. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- ^ a b Beleza, Sandra; Santos, A. M.; McEvoy, B.; Alves, I.; Martinho, C.; Cameron, E.; Shriver, M. D.; Parra, E. J.; Rocha, J. (2012). "The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 30 (1): 24–35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207. PMC 3525146. PMID 22923467.
- ^ Lalueza-Fox; Römpler, H; Caramelli, D; Stäubert, C; Catalano, G; Hughes, D; Rohland, N; Pilli, E; Longo, L; Condemi, S; de la Rasilla, M; Fortea, J; Rosas, A; Stoneking, M; Schöneberg, T; Bertranpetit, J; Hofreiter, M; et al. (2007). "A melanocortin-1 receptor allele suggests varying pigmentation among Neanderthals". Science. 318 (5855): 1453–1455. Bibcode:2007Sci...318.1453L. doi:10.1126/science.1147417. PMID 17962522. S2CID 10087710.
- ^ a b Beals, Kenneth L; Smith, Courtland L; Dodd, Stephen M (1984). "Brain Size, Cranial Morphology, Climate, and Time Machines". Current Anthropology. 25 (3): 301–330. doi:10.1086/203138.
- ^ Nowaczewska, Wioletta; Dabrowski, Pawel; Kuźmiński, Lukasz (2011). "Morphological Adaptation to Climate in Modern Homo sapiens Crania: The Importance of Basicranial Breadth". Collegium Antropologicum. 35 (3): 625–36. PMID 22053534.
- ^ Peng, Y.; et al. (2010). "The ADH1B Arg47His polymorphism in East Asian populations and expansion of rice domestication in history". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 10: 15. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-15. PMC 2823730. PMID 20089146.
- ^ Ségurel, Laure; Bon, Céline (2017). "On the Evolution of Lactase Persistence in Humans". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 18 (1): 297–319. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-091416-035340. PMID 28426286.
- ^ Ingram, Catherine J. E.; Mulcare, Charlotte A.; Itan, Yuval; Thomas, Mark G.; Swallow, Dallas M. (2008-11-26). "Lactose digestion and the evolutionary genetics of lactase persistence". Human Genetics. 124 (6): 579–591. doi:10.1007/s00439-008-0593-6. ISSN 0340-6717. PMID 19034520.
- ^ Ilardo, M. A.; Moltke, I.; Korneliussen, T. S.; Cheng, J.; Stern, A. J.; Racimo, F.; de Barros Damgaard, P.; Sikora, M.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Rasmussen, S.; van den Munckhof, I. C. L.; ter Horst, R.; Joosten, L. A. B.; Netea, M. G.; Salingkat, S.; Nielsen, R.; Willerslev, E. (2018-04-18). "Physiological and Genetic Adaptations to Diving in Sea Nomads". Cell. 173 (3): 569–580.e15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.054. PMID 29677510.
- ^ Gislén, A; Dacke, M; Kröger, RH; Abrahamsson, M; Nilsson, DE; Warrant, EJ (2003). "Superior Underwater Vision in a Human Population of Sea Gypsies". Current Biology. 13(10): 833–836. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00290-2. PMID 12747831.
- ^ Klein, Richard (1995). "Anatomy, behavior, and modern human origins". Journal of World Prehistory. 9 (2): 167–98. doi:10.1007/bf02221838.
- ^ Feierman, Jay R. (2009). The Biology of Religious Behavior: The Evolutionary Origins of Faith and Religion. ABC-CLIO. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-313-36430-3.
- ^ Soressi M. (2005) Late Mousterian lithic technology. Its implications for the pace of the emergence of behavioural modernity and the relationship between behavioural modernity and biological modernity, pp. 389–417 in L. Backwell et F. d'Errico (eds.) From Tools to Symbols, Johanesburg: University of Witswatersand Press. ISBN 1868144178.
- ^ Companion encyclopedia of archaeology (1999). Routledge. ISBN 0415213304. Vol. 2. p. 763 (cf., ... "effectively limited to organic samples" [ed. organic compounds ] "or biogenic carbonates that date to less than 50 ka (50,000 years ago)."). See also: Later Stone Ageand Upper Paleolithic.
- ^ Mellars, Paul (2006). "Why did modern human populations disperse from Africa ca. 60,000 years ago?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (25): 9381–86. Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.9381M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510792103. PMC 1480416. PMID 16772383.
- ^ Shea, John (2011). "Homo sapiens Is As Homo sapiens Was". Current Anthropology. 52(1): 1–35. doi:10.1086/658067.
- ^ McBrearty, Sally; Brooks, Allison (2000). "The revolution that wasn't: a new interpretation of the origin of modern human behavior". Journal of Human Evolution. 39 (5): 453–563. doi:10.1006/jhev.2000.0435. PMID 11102266.
- ^ Henshilwood, Christopher; Marean, Curtis (2003). "The Origin of Modern Human Behavior: Critique of the Models and Their Test Implications". Current Anthropology. 44 (5): 627–651. doi:10.1086/377665. PMID 14971366.
- ^ Marean, Curtis; et al. (2007). "Early human use of marine resources and pigment in South Africa during the Middle Pleistocene". Nature. 449 (7164): 905–908. Bibcode:2007Natur.449..905M. doi:10.1038/nature06204. PMID 17943129.
- ^ Powell, Adam; et al. (2009). "Late Pleistocene Demography and the Appearance of Modern Human Behavior" (PDF). Science. 324 (5932): 1298–1301. Bibcode:2009Sci...324.1298P. doi:10.1126/science.1170165. PMID 19498164.
- ^ Premo, Luke; Kuhn, Steve (2010). "Modeling Effects of Local Extinctions on Culture Change and Diversity in the Paleolithic". PLOS ONE. 5 (12): e15582. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...515582P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015582. PMC 3003693. PMID 21179418.
- ^ St. Fleur, Nicholas (12 September 2018). "Oldest Known Drawing by Human Hands Discovered in South African Cave". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ d'Errico, F.; Backwell, L.; Villa, P.; Degano, I.; Lucejko, J. J.; Bamford, M. K.; Higham, T. F. G.; Colombini, M. P.; Beaumont, P. B. (2012). "Early evidence of San material culture represented by organic artifacts from Border Cave, South Africa". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 109 (33): 13214–13219. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10913214D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204213109. PMC 3421171. PMID 22847420.
- ^ Mourre, V.; Villa, P.; Henshilwood, C. S. (2010). "Early Use of Pressure Flaking on Lithic Artifacts at Blombos Cave, South Africa". Science. 330 (6004): 659–62. Bibcode:2010Sci...330..659M. doi:10.1126/science.1195550. PMID 21030655.
- ^ a b Brown, Kyle S.; Marean, Curtis W.; Jacobs, Zenobia; Schoville, Benjamin J.; Oestmo, Simen; Fisher, Erich C.; Bernatchez, Jocelyn; Karkanas, Panagiotis; Matthews, Thalassa (2012). "An early and enduring advanced technology originating 71,000 years ago in South Africa". Nature. 491 (7425): 590–3. Bibcode:2012Natur.491..590B. doi:10.1038/nature11660. PMID 23135405.
- ^ Long, Jeffrey C.; Li, Jie; Healy, Meghan E. (2009). "Human DNA sequences: More variation and less race" (PDF). American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 139 (1): 23–34. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21011. hdl:2027.42/62133. PMID 19226648.
- ^ Scholz, C. A.; Johnson, T. C.; Cohen, A. S.; King, J. W.; Peck, J. A.; Overpeck, J. T.; Talbot, M. R.; Brown, E. T.; Kalindekafe, L.; Amoako, P. Y. O.; Lyons, R. P.; Shanahan, T. M.; Castaneda, I. S.; Heil, C. W.; Forman, S. L.; McHargue, L. R.; Beuning, K. R.; Gomez, J.; Pierson, J. (2007). "East African megadroughts between 135 and 75 thousand years ago and bearing on early-modern human origins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (42): 16416–21. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10416416S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703874104. PMC 1964544. PMID 17785420.
- ^ Wells, Spencer (2003). The Journey of Man: A Genetic Odyssey. Princeton, N.J. : Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691115320.
- ^ Henshilwood, Christopher; et al. (2002). "Emergence of Modern Human Behavior: Middle Stone Age Engravings from South Africa". Science. 295 (5558): 1278–1280. Bibcode:2002Sci...295.1278H. doi:10.1126/science.1067575. PMID 11786608.
- ^ Henshilwood, Christopher S.; d'Errico, Francesco; Watts, Ian (2009). "Engraved ochres from the Middle Stone Age levels at Blombos Cave, South Africa". Journal of Human Evolution. 57 (1): 27–47. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2009.01.005. PMID 19487016.
- ^ Texier, PJ; Porraz, G; Parkington, J; Rigaud, JP; Poggenpoel, C; Miller, C; Tribolo, C; Cartwright, C; Coudenneau, A; Klein, R; Steele, T; Verna, C (2010). "A Howiesons Poort tradition of engraving ostrich eggshell containers dated to 60,000 years ago at Diepkloof Rock Shelter, South Africa". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (14): 6180–6185. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.6180T. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913047107. PMC 2851956. PMID 20194764.
- ^ a b McBrearty, Sally; Brooks, Allison (2000). "The revolution that wasn't: a new interpretation of the origin of modern human behavior". Journal of Human Evolution. 39(5): 453–563. doi:10.1006/jhev.2000.0435. PMID 11102266.
- ^ Henshilwood, Christopher S.; et al. (2004). "Middle Stone Age shell beads from South Africa". Science. 304 (5669): 404. doi:10.1126/science.1095905. PMID 15087540.
- ^ d'Errico, Francesco; et al. (2005). "Nassarius kraussianus shell beads from Blombos Cave: evidence for symbolic behaviour in the Middle Stone Age". Journal of Human Evolution. 48 (1): 3–24. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2004.09.002. PMID 15656934.
- ^ Vanhaeren, Marian; et al. (2013). "Thinking strings: Additional evidence for personal ornament use in the Middle Stone Age at Blombos Cave, South Africa". Journal of Human Evolution. 64 (6): 500–517. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.001. PMID 23498114.
- ^ Backwell, L; d'Errico, F; Wadley, L (2008). "Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa". Journal of Archaeological Science. 35(6): 1566–1580. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2007.11.006.
- ^ Wadley, Lyn (2008). "The Howieson's Poort industry of Sibudu Cave". South African Archaeological Society Goodwin Series. 10.
- ^ Lombard M, Phillips L (2010). "Indications of bow and stone-tipped arrow use 64,000 years ago in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa". Antiquity. 84 (325): 635–648. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00100134.
- ^ Lombard M (2011). "Quartz-tipped arrows older than 60 ka: further use-trace evidence from Sibudu, Kwa-Zulu-Natal, South Africa". Journal of Archaeological Science. 38 (8): 1918–1930. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2011.04.001.
- ^ Backwell, L; Bradfield, J; Carlson, KJ; Jashashvili, T; Wadley, L; d'Errico, F (2018). "The antiquity of bow-and-arrow technology: evidence from Middle Stone Age layers at Sibudu Cave". Journal of Archaeological Science. 92 (362): 289–303. doi:10.15184/aqy.2018.11.
- ^ Yellen, JE; AS Brooks; E Cornelissen; MJ Mehlman; K Stewart (28 April 1995). "A middle stone age worked bone industry from Katanda, Upper Semliki Valley, Zaire". Science. 268(5210): 553–556. Bibcode:1995Sci...268..553Y. doi:10.1126/science.7725100. PMID 7725100.
- ^ Brown, Kyle S.; Marean, Curtis W.; Herries, Andy I.R.; Jacobs, Zenobia; Tribolo, Chantal; Braun, David; Roberts, David L.; Meyer, Michael C.; Bernatchez, J. (14 August 2009), "Fire as an Engineering Tool of Early Modern Humans", Science, 325 (5942): 859–862, Bibcode:2009Sci...325..859B, doi:10.1126/science.1175028, PMID 19679810
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (13 October 2011). "A Cultural Leap at the Dawn of Humanity - Ancient 'paint factory' unearthed". BBC News. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Vastag, Brian (13 October 2011). "South African cave yields paint from dawn of humanity". Washington Post. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Henshilwood, Christopher S.; et al. (2011). "A 100,000-Year-Old Ochre-Processing Workshop at Blombos Cave, South Africa". Science. 334 (6053): 219–222. Bibcode:2011Sci...334..219H. doi:10.1126/science.1211535. PMID 21998386.
- ^ Shipton C, d'Errico F, Petraglia M, et al. (2018). 78,000-year-old record of Middle and Later Stone Age innovation in an East African tropical forest. Nature Communications
- ^ Sahle, Y.; Hutchings, W. K.; Braun, D. R.; Sealy, J. C.; Morgan, L. E.; Negash, A.; Atnafu, B. (2013). Petraglia, Michael D (ed.). "Earliest Stone-Tipped Projectiles from the Ethiopian Rift Date to >279,000 Years Ago". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e78092. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...878092S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078092. PMC 3827237. PMID 24236011.
- ^ Marean, Curtis; et al. (2007). "Early human use of marine resources and pigment in South Africa during the Middle Pleistocene". Nature. 449 (7164): 905–908. Bibcode:2007Natur.449..905M. doi:10.1038/nature06204. PMID 17943129.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-01-05. Retrieved 2019-09-11.
- ^ Guinness World Records (10 September 2015). Guinness World Records 2016. Guinness World Records. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-910561-03-4.
- ^ Chatterjee, Rhitu (15 March 2018). "Scientists Are Amazed By Stone Age Tools They Dug Up In Kenya". NPR. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- ^ Yong, Ed (15 March 2018). "A Cultural Leap at the Dawn of Humanity - New finds from Kenya suggest that humans used long-distance trade networks, sophisticated tools, and symbolic pigments right from the dawn of our species". The Atlantic. Retrieved 15 March2018.
- ^ Brooks AS, Yellen JE, Potts R, Behrensmeyer AK, Deino AL, Leslie DE, Ambrose SH, Ferguson JR, d'Errico F, Zipkin AM, Whittaker S, Post J, Veatch EG, Foecke K, Clark JB (2018). "Long-distance stone transport and pigment use in the earliest Middle Stone Age". Science. 360 (6384): 90–94. Bibcode:2018Sci...360...90B. doi:10.1126/science.aao2646. PMID 29545508.
- ^ Sahle Y, Brooks AS (2018). "Assessment of complex projectiles in the early Late Pleistocene at Aduma, Ethiopia". PLOS ONE. 14 (5): e0216716. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1416716S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0216716. PMC 6508696. PMID 31071181.
- ^ https://slate.com/human-interest/2013/06/human-advancement-why-has-so-much-of-our-progress-come-so-recently.html
- ^ https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg21328571-400-puzzles-of-evolution-why-was-technological-development-so-slow/





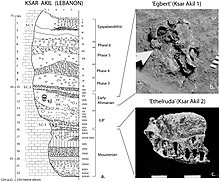
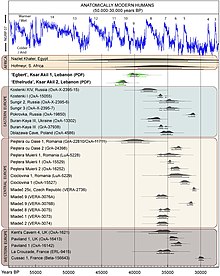






No comments:
Post a Comment